If you finish installing the QEMU-NVMe, Now You can use the newest version virtual OpenChannelSSD.
i.e You can try to use LightNVM with virtual OpenChannelSSD.
Befoer starting this process, I recommend you to read Getting started of the official lightnvm site.
As you can see the official lightnvm site.
you can know the following :
-
What version of linux support lightnvm ?
-
What tool do you need to install LightNVM on QEMU-NMVe. ?
-
Of course. How Can I install ane execute QEMU-NVMe for OpenChannelSSD ?
First, I realized What I misunderstan about virt-manager.
I think, with GUI,virt-manager, I can use QEMU-NVMe with virt-Manager. But I realized that is wrong.
from Redhat site written in 20 Apr 2016 on redHat board.
Becuase, When you use virtualization of kernel, you use Libvirt(the virtualization API).
So Libvirt of Redhat on CentOS 7 doesn’t even support it explicitly yet. So I can understan I have to use command Line to execute NVMe device. i.e virt-manager doesn’t support how to add NVMe device.
So I will use QEMU-NVMe for openchannelSSD on command line.
Before starting installing lighiNVM, so far, I will brief what I have done about QEMU-KVM and QEMU-NVMe.
Summary of installing QEMU-KVM on HOST OS
$ sudo yum install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install (virt-viewer)
-- instead of the above command, I recommend you to contain virt-viewer. rather, you have to install something related to virt-viewer. So what I recommend is :
$ sudo yum install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer
$ reboot OR shutdown -r now
$ virt-manager
The above command is basic setting to execute QEMU-KVM with GUI, virt-manager tool.
And if you want to how to install GUEST OS, please see my blog’s QEMU-URL
Of course, When you install “Development Tools” with yum to compile kernel.
If you don’t install “Development Tools”, please add one line first like this
$ sudo yum groupinstall “Development Tools”
Summary of install and compiling QEMU-NVMe for OpenChannelSSD on HOST OS
- first you need to install Qemu-nvme
- If you already installed "Development tools", just do it as follows.
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/qemu-nvme.git
$ cd qemu-nvme
- this is my chocie when I evaluate FIO 4k ramdomwrit T1Q256 FOX(fresh of box)
$ ./configure --python=/usr/bin/python2 --enable-kvm --target-list=x86_64-softmmu --enable-linux-aio --prefix=$HOME/qemu-nvme
- At this time. You find error
- solution for that is below
$ sudo yum install -y gtk2-devel OR $ sudo yum install libaio-devel
- One more time, ./configure ~~~ . After that
$ make -j8
$ sudo make install
- if you want to use Ramdisk
$ mkdir ./ramdisk OR $ mkdir ./rootOfRamdisk
$ sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=7G tmpfs ./ramdisk OR $ sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=7G tmpfs ./rootOfRamdisk
$ cd ramdisk OR $ cd rootOFRamdisk
- for Qemu-nvme
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=./blknvme bs=1G count=4
$ ~/qemu-nvme/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 -m 16G -smp 4 --enable-kvm -hda /var/lib/libvirt/images/vDisk.qcow2(virtual device) -drive file=./blknvme(virtual nvme),if=none,id=mynvme -device nvme,drive=mynvme,serial=deadbeef,lver=1,~~~(another option) -monitor stdio
- For example command
$ ~/qemu-nvme/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 -m 16G -smp 4 --enable-kvm -hda /var/lib/libvirt/images/vDisk.qcow2 -drive file=./blknvme,if=none,id=mynvme -device nvme,drive=mynvme,serial=deadbeef,lver=1,ll2pmode=0,lnum_lun=4,lnum_pln=2,lsecs_per_pg=4,lpgs_per_blk=512 -monitor stdio
GuestOS’s status of QEMU-KVM before installing QEMU-NVMe.
On QEMU-KVM, you can perceive NVMe device and PCI related to NVMe.
But on QEMU-NVMe, the everything is perceived. it’s amazing,
The following is status of lspci, lsblk, uname, dmesg, ls /dev to check if there is NVMe device on QEMU-KVM
i.e the following data is measured on GUEST OS
Kernel Version
$ uname -a
Linux localhost.localdomain 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Nov 19 22:10:57 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
$ cat /etc/centos-release
CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core)
dmesg | grep ‘nvm’
$ dmesg | grep 'nvm'
There is nothing to print
lspci -vt
$ lspci -vt
-[0000:00]-+-00.0 Intel Corporation 440FX - 82441FX PMC [Natoma]
+-01.0 Intel Corporation 82371SB PIIX3 ISA [Natoma/Triton II]
+-01.1 Intel Corporation 82371SB PIIX3 IDE [Natoma/Triton II]
+-01.3 Intel Corporation 82371AB/EB/MB PIIX4 ACPI
+-02.0 Red Hat, Inc. QXL paravirtual graphic card
+-03.0 Red Hat, Inc Virtio network device
+-04.0 Intel Corporation 82801FB/FBM/FR/FW/FRW (ICH6 Family) High Definition Audio Controller
+-05.0 Red Hat, Inc Virtio console
+-06.0 Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) USB UHCI Controller #1
+-06.1 Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) USB UHCI Controller #2
+-06.2 Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) USB UHCI Controller #3
+-06.7 Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) USB2 EHCI Controller #1
+-07.0 Red Hat, Inc Virtio block device
\-08.0 Red Hat, Inc Virtio memory balloon
lsblk
$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
vda 252:0 0 32G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 500M 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 31.5G 0 part
├─centos-root 253:0 0 28.3G 0 lvm /
└─centos-swap 253:1 0 3.2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
ls /dev
$ ls /dev
autofs fd mqueue snapshot tty19 tty35 tty51 ttyS1 vcsa
block full net snd tty2 tty36 tty52 ttyS2 vcsa1
bsg fuse network_latency sr0 tty20 tty37 tty53 ttyS3 vcsa2
btrfs-control hidraw0 network_throughput stderr tty21 tty38 tty54 uhid vcsa3
bus hpet null stdin tty22 tty39 tty55 uinput vcsa4
cdrom hugepages nvram stdout tty23 tty4 tty56 urandom vcsa5
centos initctl oldmem tty tty24 tty40 tty57 usbmon0 vcsa6
char input port tty0 tty25 tty41 tty58 usbmon1 vda
console kmsg ppp tty1 tty26 tty42 tty59 usbmon2 vda1
core log ptmx tty10 tty27 tty43 tty6 usbmon3 vda2
cpu loop-control pts tty11 tty28 tty44 tty60 usbmon4 vfio
cpu_dma_latency lp0 random tty12 tty29 tty45 tty61 vcs vga_arbiter
crash lp1 raw tty13 tty3 tty46 tty62 vcs1 vhost-net
disk lp2 rfkill tty14 tty30 tty47 tty63 vcs2 virtio-ports
dm-0 lp3 rtc tty15 tty31 tty48 tty7 vcs3 vport1p1
dm-1 mapper rtc0 tty16 tty32 tty49 tty8 vcs4 vport1p2
dri mcelog sg0 tty17 tty33 tty5 tty9 vcs5 zero
fb0 mem shm tty18 tty34 tty50 ttyS0 vcs6
How to insatll and set up LightNVM on QEMU-NVMe for OpenChannelSSD on GUETOS
AS you can see getting started of Lightnvm.io
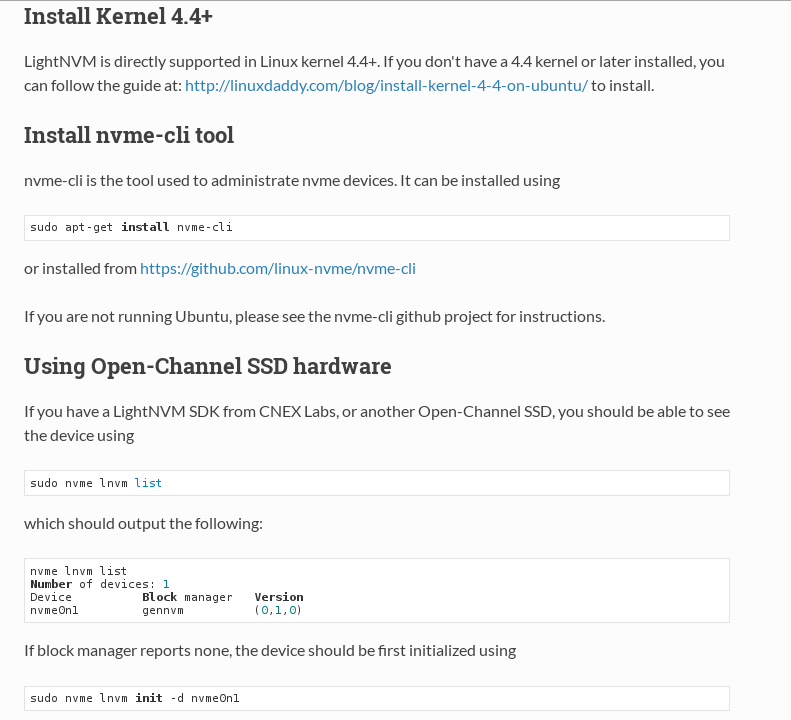
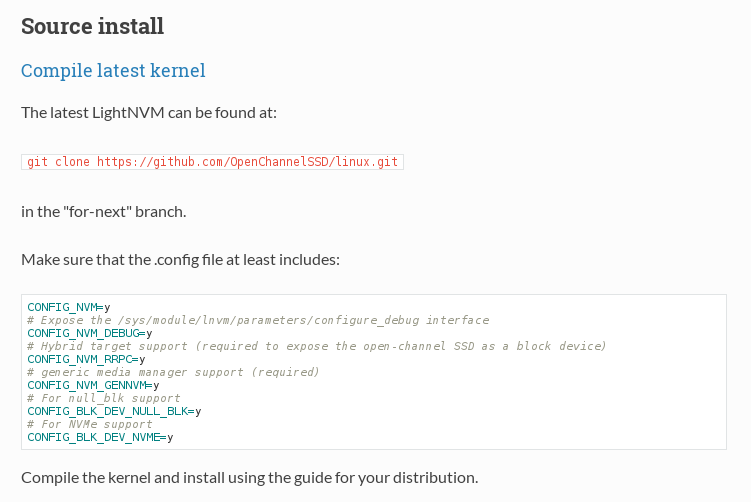
the portion of install kernel 4.4+ in getting started of LightNVM.
You can find “LightNVM is directly supported in Linux kernel 4.4+.”
So you need kernel above 4.4+ version. Fortunately, LightNVM guys manage kernel source for OpenChannleNVMe and LightNVM

Also You need lnvm tool. as you can see the above figure.
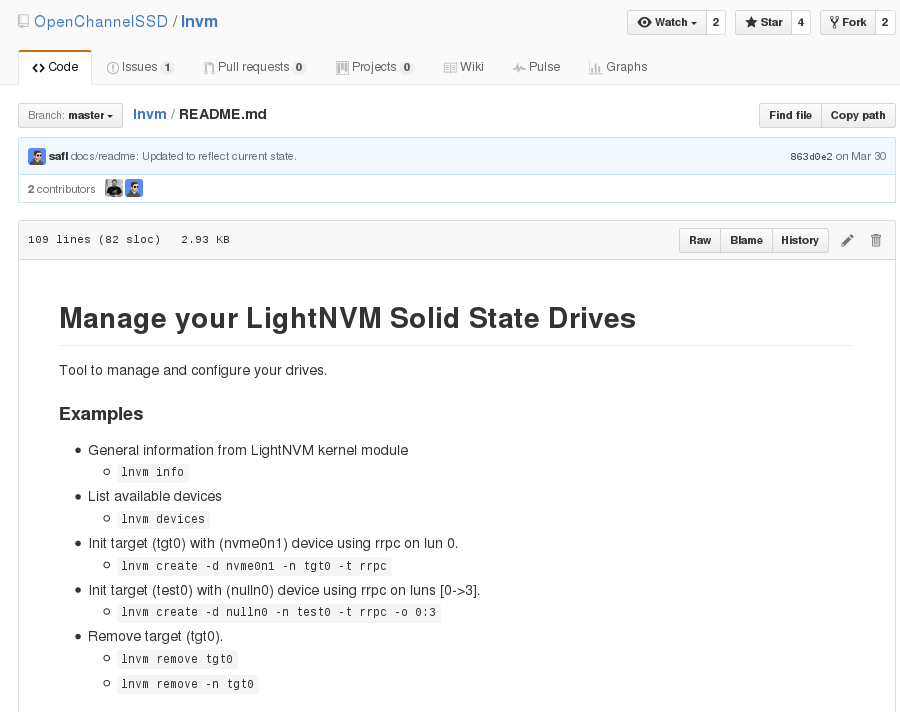
As you can see the above image. You know How to run lnvm tool. Aslo You can check how to use lnvm tool in LightNVM site’s Command Line
To sum up, lnvm tool connect among NVMe driver, generic media driver and target.
i.e you can make your own FTL like pblk and your own generic driver to fit your device(SSD).
After that, Through lnvm, You connect each other(target and media manager).
Before using the lnvm tool, you have to get sudo privilege.
From now on, let’s install and kernel complie for LightNVM and OpenChannelSSD
The newest Kernel compile on GUESTOS of QEMU-NVMe.
Also LightNVM guys manage Linux kernel support of OpenChannelSSD.
first git clone and kernel build on GuestOS
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/linux.git
cd linux
cp /.config(The Original location) /.config(OpenChannelSSD’s Linux)
make olddefconfig
make -j8
sudo make modules_install
sudo make install
be careful when you choose options in menuconfig
the following is based on rrpc but currently I evaluate on pblk.
CONFIG_NVM=y
CONFIG_NVM_DEBUG=Y
CONFIG_NVM_GENNVM=y
CONFIG_NVM_RRPC=y
The above four things is the same.
BUT, I divided into two cases.
One is :
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NULL_BLK=m
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=m
The other is :
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NULL_BLK=m
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=y
That doesn’t matter When it comes to creating lightNVM targets and device.
If you detect a problem. I recommend you that You will install once again after erase the several file
Those files is :
bbtable.qemu & blkbme(virtual device) & meta.qemu
but if you consider symbol dependency, when you build kernel.
I will explain you based on pblk
CONFIG_NVM=y
# Expose the /sys/module/lnvm/parameters/configure_debug interface
CONFIG_NVM_DEBUG=y
# Target support (required to expose the open-channel SSD as a block device)
CONFIG_NVM_PBLK=y
# Do not perform recovery upon boot (Disables recovery of the mapping table upon boot. Disable when using across boots)
CONFIG_NVM_PBLK_NO_RECOV=y
# generic media manager support (required)
CONFIG_NVM_GENNVM=y
# For NVMe support
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=y
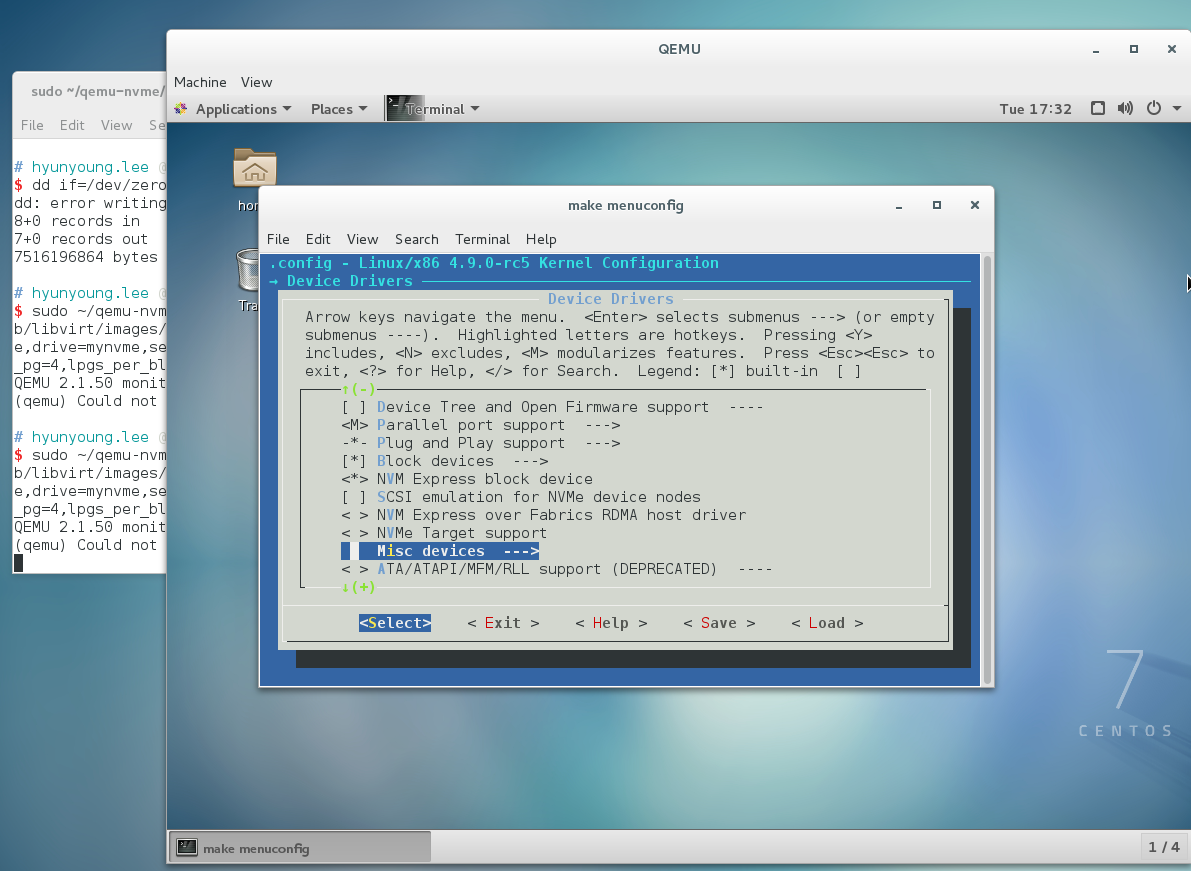
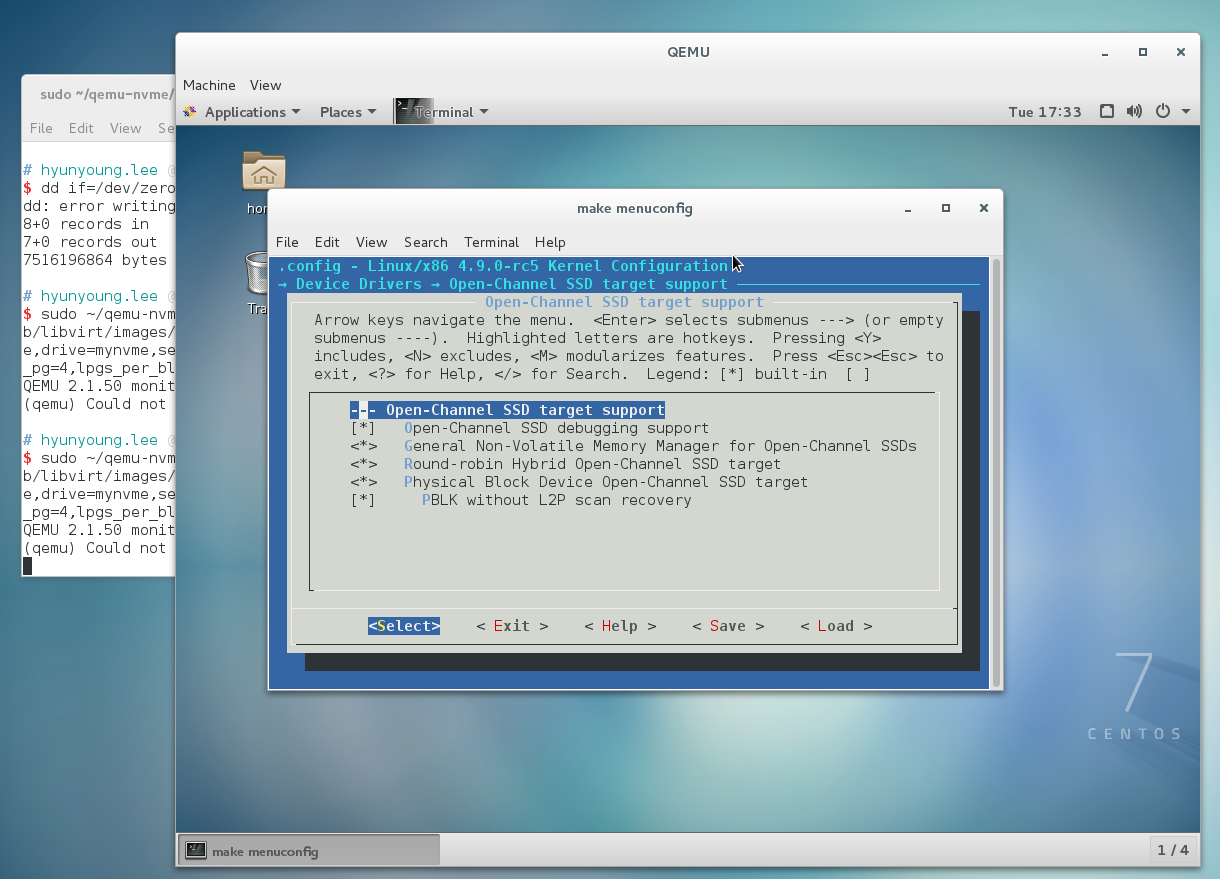
as you can see the above.
# For NVMe support CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NVME=y has dependency of symbol.
So I recommend you
in make menuconfig, Device Drivers-> NVM EXPRESS block device should be [*].
maybe if you want to check up what is different when it is done or not.
I recommend you that
you can understand olddefconfig meaning and symbol dependency.
Second usage of lnvm on GuestOS
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/lnvm.git
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/lnvm.git
Cloning into 'lnvm'...
remote: Counting objects: 80, done.
remote: Total 80 (delta 0), reused 0(delta 0), pack-reused 80
$ cd lnvm/
from here, the whole thing is impelemented in lnvm directory
$ ls
debian Documentation LICENSE linux lnvm.c Makefile README.md
$ make
cc -m64 -std=gnu99 -02 -g -pthread -D_GNU_SOURCE -Wall lnvm.c -lm -o lnvm
$ usdo make install
install -d /usr/local/sbin
install -m 755 lnvm /usr/local/sbin
When using lnvm tool, error can happen like this
$ lnvm devices
Failed to open LightNVM mgmt /dev/lightnvm/control. Error: -1

At that time, just change command like this
$ sudo ./lnvm devices
Number of devices: 1
Device Block manager version
nvme0n1 none (0,0,0)
the following is the same error and solution.
$ lnvm info
Failed to open LightNVM mgmt /dev/lightnvm/control. Error: -1
$ ./lnvm info or $ ./lnvm -d init -d nvme0n1
Failed to open LightNVM mgmt /dev/lightnvm/control. Error: -1
$ sudo ./lnvm info
LightNVM (1,0,0). 2 target type(s) regitstered
Type Version
pblk (1,0,0)
rrpc (1,0,0)
$ lnvm init -d nvme0n1
Failed to open LightNVM mgmt /dev/lightnvm/control. Error: -1
The followings is the final command to connect among NVMe driver, media manager and target
$ sudo ./lnvm init -d nvme0n1
$ sudo ./lnvm create -d nvme0n1 -n hyun -t rrpc (-o 0:3)
-o means the number of lnus.
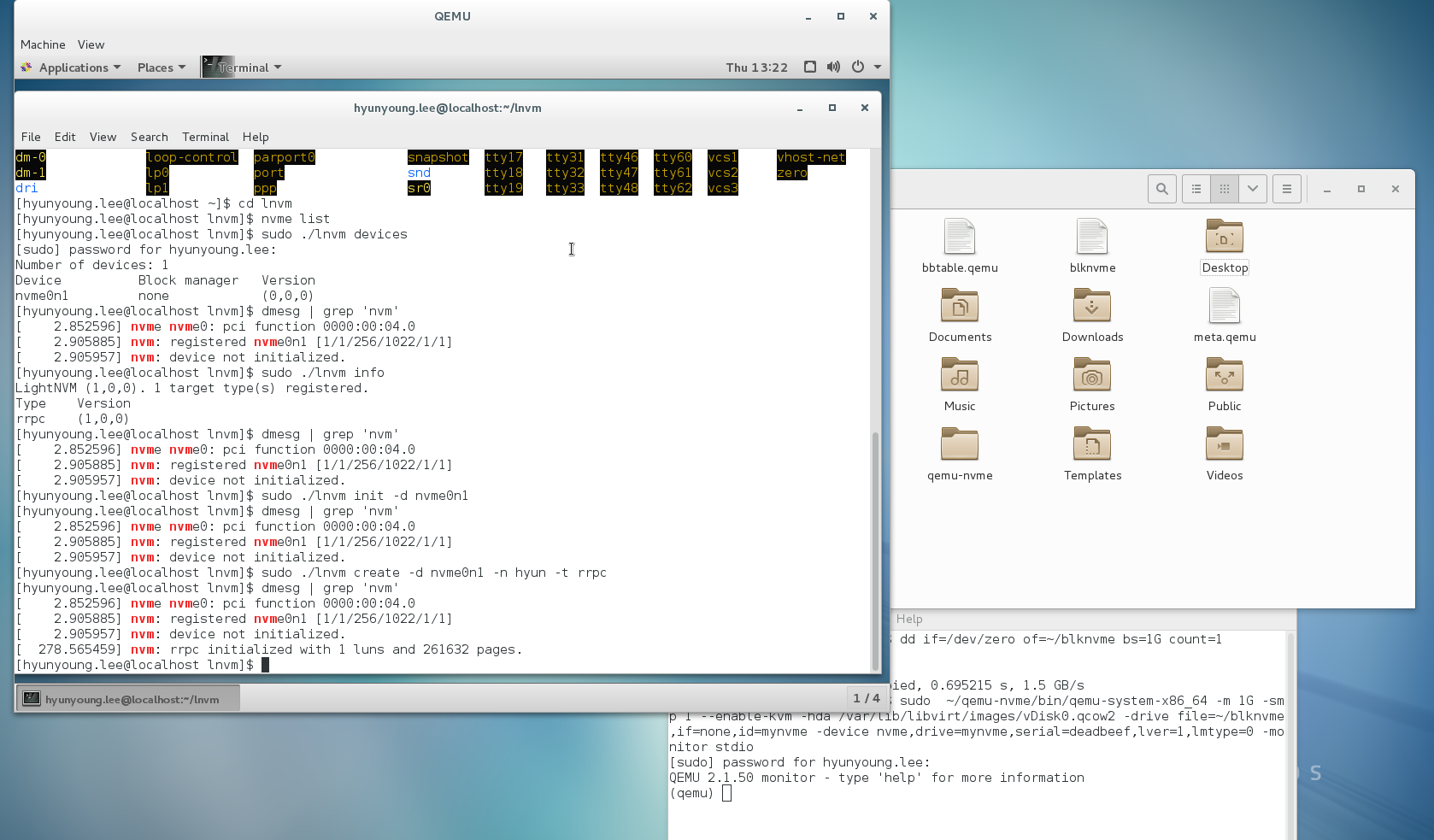
if you type lsblk on command line, you can check hyun device generated on blknvme with dd command.
Be careful, when you make target and boot with QEMU-NVMe, you have to do that in directory contain blknvme that is virtual NVMe device.
So, meta.qemu and badblock table is created. when turning on kernel with QEMU-NVMe and creating target like this.
currently, you can see meta.qemu
blknvme and metat.qemu file appears.
$ ls
bbtable.qemu blknvme meta.qemu

Summary of installing lightNVM and compiling kernel on GUESTOS of QEMU-NVMe
On GEUST OS (Ctrl+Alt+G)
- You have to install linux for openchannelSSD
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/linux.git
- After the above, You have to install kernel.
- cp /.config(The Original location) /.config(OpenChannelSSD's Linux)
- make oldconfig or olddefconfig
- make menucofig -> configuration for LihgtNVM pblk
- make -j8
- sudo make modules_install
- sudo make modules
- for lnvm
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/lnvm.git
$ cd lnvm
$ make
$ sudo make install
- After completing installation of lnvm, for looking at usage
- in lnvm directory
$ sudo ./lnvm --help
$ sudo ./lnvm info
$ sudo ./lnvm devices
$ sudo ./lnvm init -d nvme0n1
$ sudo ./lnvm create -d nvme0n1 -n hyun(target name) -t pblk -o 0:3
$ sudo ./lnvm remove -n hyun(targer name)
Summary of the whole process to use lightNVM on QEMU-NVMe
as of 20161205.
On host side
- If you don't install qemu-kvm, first, You have to install that tool
$ sudo yum install -y qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install (virt-viewer)
$ reboot
$ virt-manager
- first you need to install Qemu-nvme
- If you already installed "Development tools", just do it as follows.
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/qemu-nvme.git
$ cd qemu-nvme
$ ./configure --python=/usr/bin/python2 --enable-kvm --target-list=x86_64-softmmu --enable-linux-aio --prefix=$HOME/qemu-nvme
- At this time. You find error
- solution for that is below
$ sudo yum install -y gtk2-devel OR $ sudo yum install libaio-devel
- One more time, ./configure ~~~ . After that
$ make -j8
$ sudo make install
- if you want to use Ramdisk
$ mkdir ./ramdisk OR $ mkdir ./rootOfRamdisk
$ sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=7G tmpfs ./ramdisk OR $ sudo mount -t tmpfs -o size=7G tmpfs ./rootOfRamdisk
$ cd ramdisk OR $ cd rootOFRamdisk
- for Qemu-nvme
$ dd if=/dev/zero of=./blknvme bs=1G count=4
$ sudo ~/qemu-nvme/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 -m 16G -smp 4 --enable-kvm -hda /var/lib/libvirt/images/vDisk.qcow2(virtual device) -drive file=./blknvme(virtual nvme),if=none,id=mynvme -device nvme,drive=mynvme,serial=deadbeef,lver=1,~~~(another option) -monitor stdio
- For example command
$ sudo ~/qemu-nvme/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 -m 16G -smp 4 --enable-kvm -hda /var/lib/libvirt/images/vDisk.qcow2 -drive file=./blknvme,if=none,id=mynvme -device nvme,drive=mynvme,serial=deadbeef,lver=1,ll2pmode=0,lnum_lun=4,lnum_pln=2,lsecs_per_pg=4,lpgs_per_blk=512 -monitor stdio
On GeustOS(Ctrl+Alt+G)
- You have to install linux for openchannelSSD
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/linux.git
- After the above, You have to install kernel.
- cp /.config(The Original location) /.config(OpenChannelSSD's Linux)
- make oldconfig or olddefconfig
- make menucofig -> configuration for LihgtNVM pblk - you always have to check getting started of lighinvm to know what option is to use LightNVM and OpenChannelSSD.
- make -j8
- sudo make modules_install
- sudo make modules
- for lnvm
$ git clone https://github.com/OpenChannelSSD/lnvm.git
$ cd lnvm
$ make
$ sudo make install
- After completing installation of lnvm, for looking at usage
$ sudo ./lnvm --help
$ sudo ./lnvm info
$ sudo ./lnvm devices
$ sudo ./lnvm init -d nvme0n1
$ sudo ./lnvm create -d nvme0n1 -n hyun(target name) -t pblk -o 0:3
$ sudo ./lnvm remove -n hyun(targer name)
- Simple test with Fio
- Installation of fio
- fio options in shell script
BLOCKSIZE=4k
RW=randwrite
for REPEAT in $(seq 0 9)
do
fio --name=${BLOCKSIZE}-${RW}-${REPEAT} \
--filename=/dev/nvme0n1 \
--rw=randwrite \
--bs=4096 \
--ioengine=libaio \
--numjobs=1 \
--iodepth=256 \
--direct=1 \
--thread \
--write_iops_log=${BLOCKSIZE}-${RW}-${REPEAT} \
--log_avg_msec=1000 \
--size=$((900*1024*1204)) or --size=50% or Noone
done
Reference
-
lightnvm.io - the official site of lightnvm
The following is explaining How to add NVMe device by virt-manager, the answer is you cannot use virt-manger.
Source code for openchannelSSD
Appendix A : build Kernel to latest version
AS of 20161123 below image is changed for pblk on officail site of lightNVM
In order to work on lightnvm, I need kernel above version 4.4+.**
I will install kernel version latest version
you remeber the above image is change to fit pblk on the officail site of lightNVM
In my build process
su
chmod u+w /etc/sudoers
vim /etc/sudoers
chmod u-w /etc/sudoers
sudo yum install -y gcc bc openssl-devel ncurses-devel pciutils libudev-devel
wget https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v4.x/linux-4.8.tar.xz
xz -cd linux-4.X.tar.xz | tar xvf -
$ cp ./Downloads/config-4.8.0-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 ./linux-4.8/.config
$ cd linux-4.8/
(make oldconfig)
$ make menuconfig
$ make
$ make modules_install install
($ grep ^menuentry /boot/grub2/grub.cfg | cut –d\’ –f2)
$ grub2-editenv list
$ grub2-set-default 0
$ sudo grep ^menuentry /boot/grub2/grub.cfg | cut –d\’ –f2
cut: you must specify a list of bytes, characters, or fields
Try 'cut --help' for more information.
[sudo] password for hyunyoung.lee:
-- configure procedure of booting kernel.
$ sudo grub2-editenv list
saved_entry=CentOS Linux (3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64) 7 (Core)
$ sudo grub2-set-default 0
kernel build to latest version with OpenchannelSSD
Appendix B
The following is build mainline kerenl of ELRepo on HostOS
$ sudo rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
$ sudo rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
Retrieving http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
Preparing... ################################# [100%]
Updating / installing...
1:elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo ################################# [100%]
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-ml
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
elrepo | 2.9 kB 00:00
elrepo-kernel | 2.9 kB 00:00
(1/2): elrepo/primary_db | 376 kB 00:00
(2/2): elrepo-kernel/primary_db | 1.6 MB 00:00
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos-distro.1gservers.com
* elrepo: elrepo.org
* elrepo-kernel: elrepo.org
* epel: linux.mirrors.es.net
* extras: mirrors.usc.edu
* updates: centos.sonn.com
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package kernel-ml.x86_64 0:4.8.1-1.el7.elrepo will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
......
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel update
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos-distro.1gservers.com
* elrepo: repos.lax-noc.com
* elrepo-kernel: repos.lax-noc.com
* epel: mirror.prgmr.com
* extras: mirrors.usc.edu
* updates: centos.sonn.com
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package python-perf.x86_64 0:3.10.0-327.36.2.el7 will be updated
---> Package python-perf.x86_64 0:4.8.1-1.el7.elrepo will be an update
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Updating:
python-perf x86_64 4.8.1-1.el7.elrepo elrepo-kernel 443 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
......