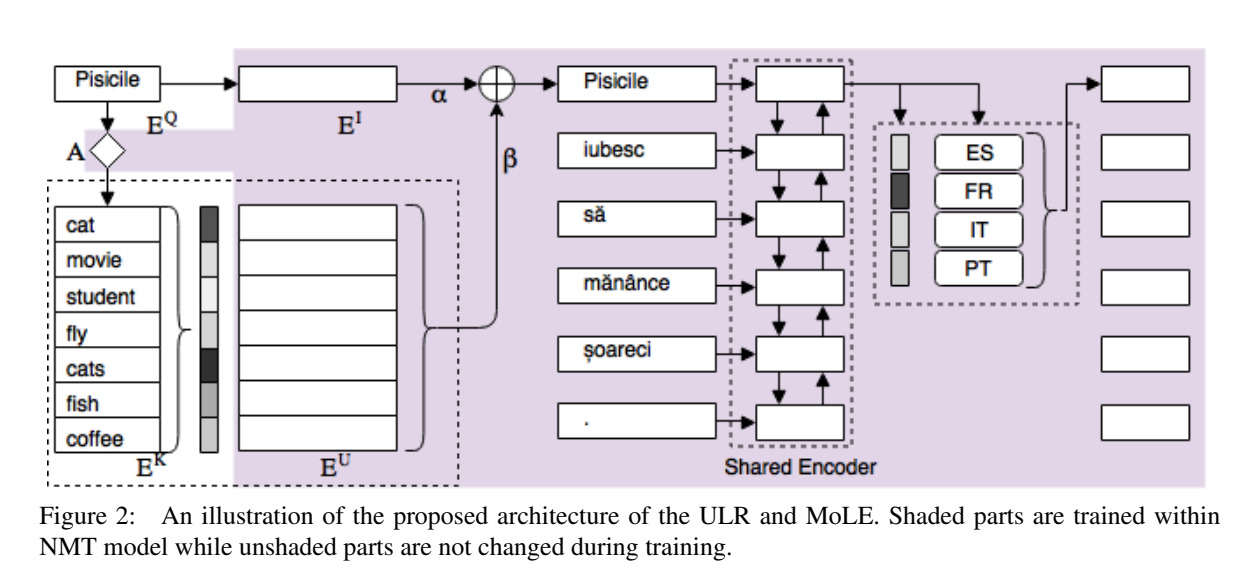
This is a brief summary of paper for me to note it, Universal Neural Machine Translation for Extremely Low Resource Languages. Gu et al. NAACL 2018
They proposed the model which is useful at low-resource language pair in machine translation.
Auxiliary languages are used to extracter universal token embedding and sentence embeddding.
To sum up, they approach utilizes multi-lingual neural translation system to share lexical and sentence level representations across multiple source languages into one target language:
In figure above, the part shaded is learned for NMT training process.
Their model has two key points.
(1) Lexical-level Sharing
Conventionally, a multilingual NMT model has a vocabulary that represents the union of the vocabularies of all source languages. Therefore, the multi-lingual words do not practically share the same embedding space since each word has its own representation. This does not pose a problem for languages with sufficiently large amount of data, yet it is a major limitation for extremely low resource languages since most of the vocabulary items will not have enough, if any, training examples to get a reliably trained models.
A possible solution is to share the surface form of all source languages through sharing sub-units such as subwords or characters. However, for an arbitrary lowresource language we cannot assume significant overlap in the lexical surface forms compared to the high-resource languages. The low-resource language may not even share the same character set as any high-resource language. It is crucial to create a shared semantic representation across all languages that does not rely on surface form overlap.
(2) Sentence-level Sharing
It is also crucial for lowresource languages to share source sentence representation with other similar languages. For example, if a language shares syntactic order with another language it should be feasible for the lowresource language to share such representation with another high recourse language. It is also important to utilize monolingual data to learn such representation since the low or zero resource language may have monolingual resources only.
They aslo showed that it is more reasonable to have similar languages as auxiliary languages.
The paper: Universal Neural Machine Translation for Extremely Low Resource Languages. Gu et al. NAACL 2018