This pase is summary of my class of Advancee Topics in computer science about MinHashing for Security Field’s file similarity.
Before going through Minhashing, arrange the background knowledges like
- What is the metric for whether data poits (X1, X2, …) in high dimensional space is similar or not?
The metric is distance, so We need the definition which quantifies the distance between X1 and X2.
i.e. finding all pairs of data point(Xi, Xj) that are within some distance threshold d(X1, X2) <= S(threshold)
When finding all paris of data point against data point Xi which is near-neighbor, it takes O(N^2).
- N is the number of data point.
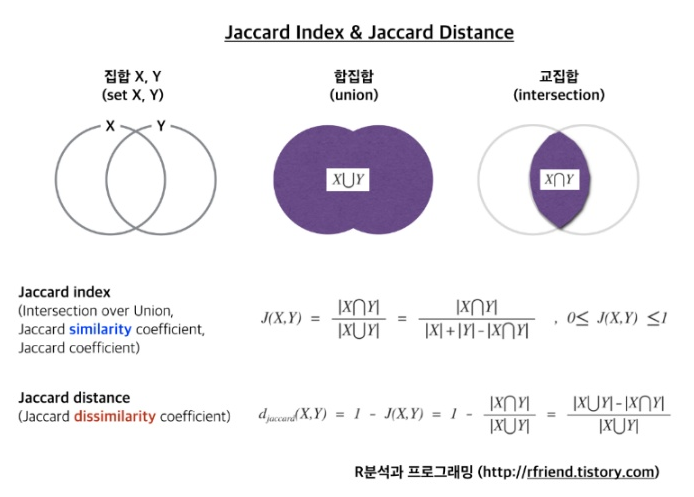
here distance metric means Jaccard distance and similarity, The relationship between Jaccard distance and Jaccard similarity is :
D(C1, C2) = 1 - Sim(C1, C2)
-
C1, C2 : set
-
D(C1, C2) : Jaccard distance in the figuer below
-
Sim(C1, C2): Jaccard similarity(Index) in the figure below - in two sets, The size of their intersection divided by the size of their union.
Let’s see an example:
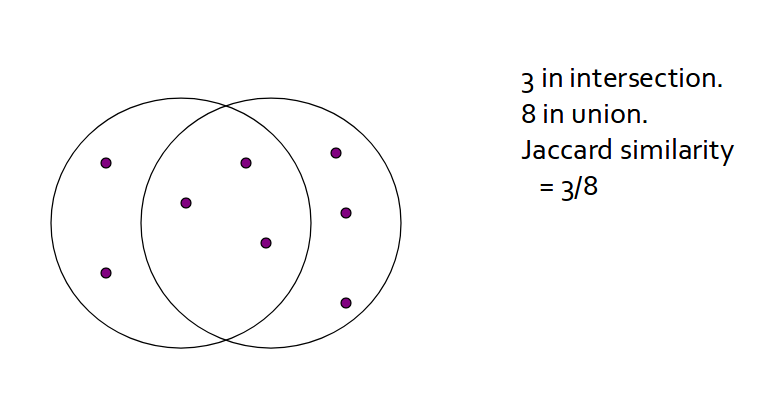
As you can see above, Jaccard similarity is 3/8.
3 is intersection set and 8 is union set.
** Keep in mind set is no-duplicate ***
Shingles
For now, We know What is distance and similairity metric on relationship of set.
Let’s see how to covert document to sets.
The simple way is :
- Document is the set of words appearing in document.
So we could represent the document as set of important words.
But There are problems which is what is the standard of importance and the set of important words ignore the ordering of words.
Shingle accounts for The ordering of words.
a K-Shingle (or K-gram) for a document si a sequence of K tokens that appear in the document.
- Tokens can be characters, words or something else, depending on the application.
Let’s suppose here tokens is characters.
K=2 , document D1 = abcab
-
Set of 2-shingles: S(D1) = {ab, bc, ca}
-
But bag of 2-shingles: S`(D1) = {ab, bc, ca, ab}, count ab twice.
So as to compress long shingles, I can hash them(2-shingle) to 4 bytes(int)
- Hash the 2-singles above: h(D1) = {1,5,7,9}
Document D1 is a set of its k-shingles C1 = s(D1)
-
Equivalently, each document is a 0/1 vector in the space of k-shingles
-
Each unique shingle is a dimension
-
Vectors are very sparse
-
In the case above, Documents that ahve a lot of shingles in common have similar text, even if the text appears in different order.
From now on, We utilize Set of shigles for Minhashing.
Minhashing
If you have a set of k-shingles for documents, encode sets using 0/1 (bit, boolean) vectors.
-
One dimension per element in the universal set.
-
interpret set intersection as bitwise AND, and set union as bitwise OR
as follows :
-
Example: C1 = 10111; C1 = 10011
-
Size of Intersection is equal to 3, size of union is 4.
-
Jaccard Similarity(not distance) = 3/4
-
Distance: d(C1, C2) = 1 - Jaccard Similarity = 1/4
-
Let’s make boolean Matrices
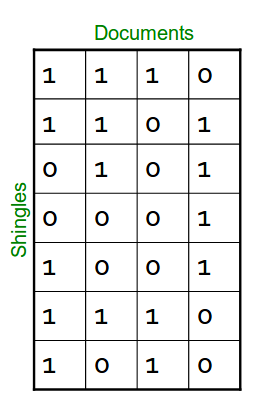
As you can see above, Column similarity is the Jaccard similairity between corresponding sets.
But There is a problem which is the matrix is sparse!
In the matrix above, column from left to right is 1,2,3,4,
Let’s calculate sim(C1, C2) of Jaccard similarity
sim(C1, C2) = intersection of C1 and C2 / union of C1 and C2 = 3/6
D(C1, C2) = 1 - 3/6 = 1/2
To sum up
so far:
-
A Document is represented into Sets of shingles
-
Shingles can be turn into boolean vector in a matrix.
From now on, Next goal is finding similar columns while computing small signatures.
- similarity of columns is similar to similarity of signatures.
Small signature means reduction of dimension.
If you want to find out similarity of two colums, use signature which is small columns than the original columns.
But When comparing all pairs may take too long time. it is solved with LSH(Locality Sensitive Hashing) which will be, later on, posted
In comparing small signature, false negative could happen unlike Bloom filter.
This means there is option which is to check that columns with simliar columns are really similar.
How to find hash function for Minhashing
-
goal: find a hash function h(C) such that:
- if sim(C1, C2) is high, then with high probability. h(C1) = h(C2) - if sim(C1, C2) is low, then with high probability. h(C1) != h(C2)
This hash function depends on the similarity metric like Jaccard Similarity called Min-Hashing.
For Min-hashing. create permutation of the rows of the boolean matrix.
When you create signature matrix, Use several independent hash function(that is, permutations) to create a signature of a column.
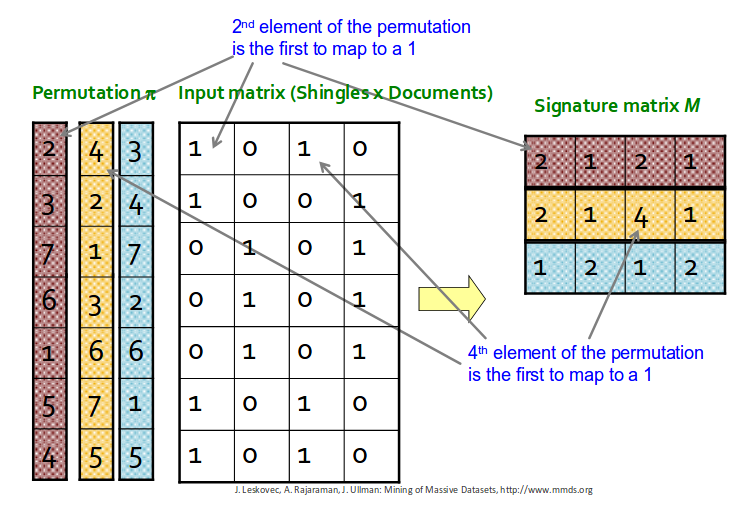
As you can see above, define Min-Hashing function for the row permuation like this:
- Min-Hashing function, H(C) = index of the first(in permuted order) in which column has value 1.
the number of permutation is equal to the number of dimension in signature matrix.
Let’s calculate similarity of pairs in a signature matrix like this :
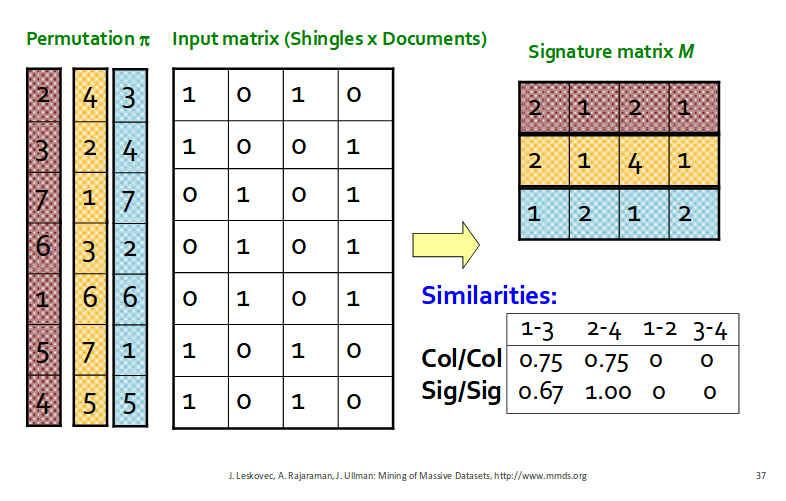
As you can see the simllarities table, similarity of two columns in the original is similar to similarity of two columns in the sigature matrix.
If you want to know Minhashing in detail, look at the Youtube below
And I recommend you a site, which is Minig of Massive Datasets, The site provide you lecture and PDF, PPT related to this article in addition to other good materials.