This article refers to OpenChannel SSDs : Linux Con Vault 2016
javigon’s blog introduces about lightnvm
Basic concept of OpenchannelSSD
Basically, I briefly arranged the contents in my blog,ligthvnm
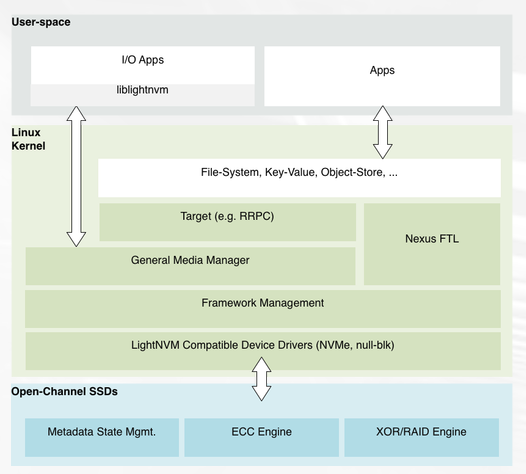
But, while I evaluate lightnvm on QEMU-NVMe, what I’m confusing exits. So, from now on, again I will arraged the concept of OpenChannelSSD. Before comparing pblk with rrpc.
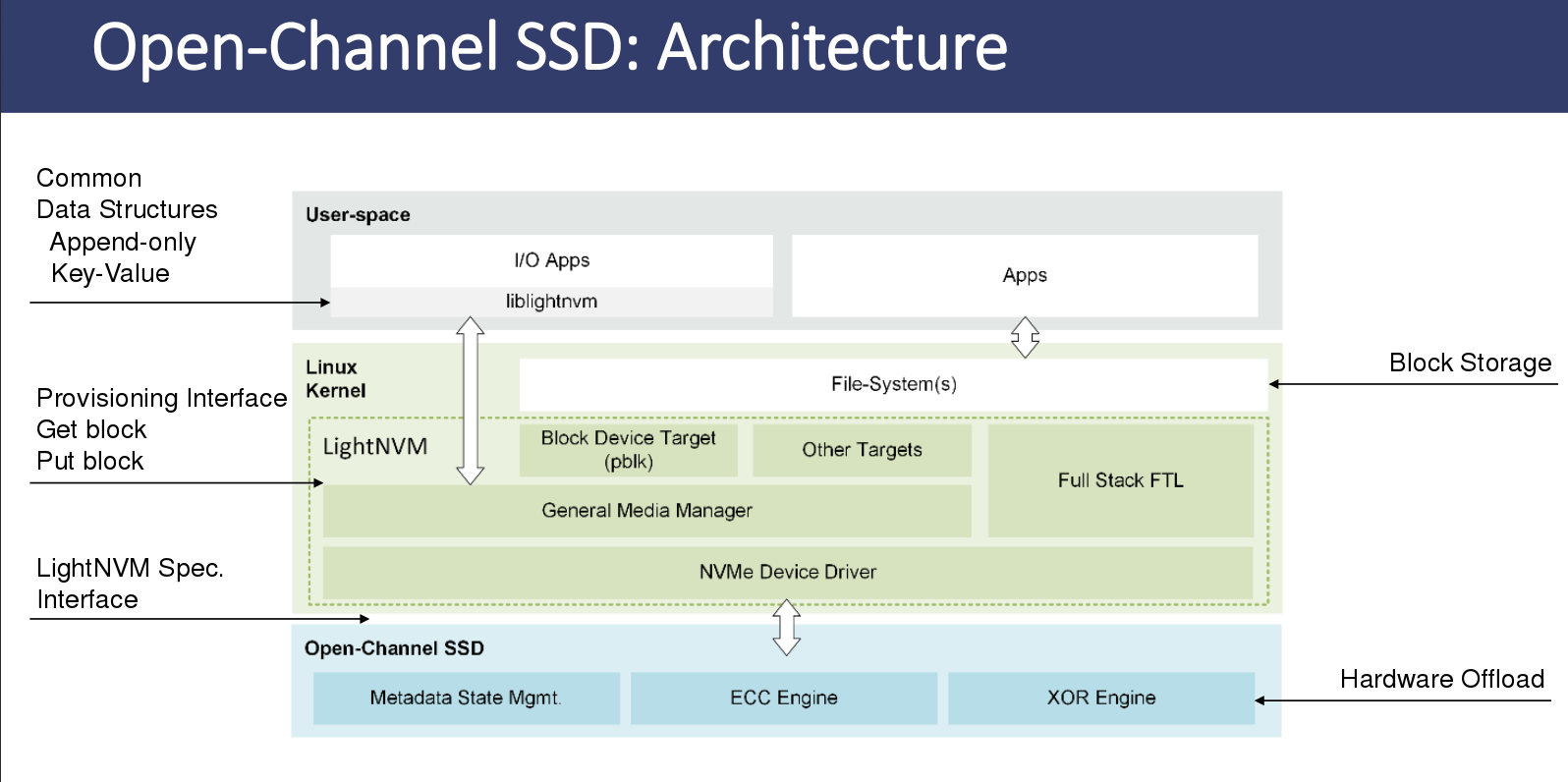
What I confuse is first what role Media Managers and Targets is. everyone as you can see the abover figure from the officail site of OpenChannelSSD
this article is written before look into code.
on the officail site,
the responsibilities are shared such that the host manages data placement, garbage collection, and I/O scheduling.
while the device manages bad blocks, durability, and implement efficient hardware engies for writing to the non-volatile memories it has attached.
from now on, just explain to you host architecture of lightnvm
Device driver.
This is similar to the ordinary device driver.
But, I think in here that device driver deal with physical address changed in device manager from logical address to physical address. i.e Physical page Address command set is handled.
So as you can read the official site, that kind of physical page address command set is as follows :
-
identify structure, used by the host to discover available features, extensions, and charateristics of an open-channel device;
- I think this meaning is like dealing with command such as device specific command
-
Physical data commands to communicate efficiently with the storage non-volatile media.
- I think this meaning is read and writ command of data with pysical address on SSD
General Media Manager(gennvm)
As you can read the article of officail site, that’s responsibility is as follows :
-
Name mapping between vendor specific and generic addresssing format
-
I think this meaning is transfer logical addressing format to Physical that vedors define like FTL
-
on the other hand, in here Whether name mapping is address mapping or not, I’m confusing.
-
-
device-specifc SSD state management (if not implemented at the device-side)
- I think this meaning is like bad block management.
-
recovery - to guarantee durability when manipulating the metadata associated with SSD state management
- I think this meaning is ECC.
-
Finally, by officail site’s article, LightNVM general media manager implements minimal block management and lets targets or user space application perform the actual FTL.
-
It is possible for a media manager to implement the whole FTL and manage user-space interfaces.
- I think after reading the above two sentence, what i understand is that generic media manager of lihgt includes FTL and user-space interface(liblightnvm), in addition, slightly minimal block management, So i.e a media manager would manage functionalities such as data placement, garbage collection, and block management.
Targets
- I think targets implement FTL functionality(e.g tlanslation logic, date placement, or garbage collection),To sum up. lightnvm place generic manager inside host, So we need to interface to have a conversation with storage interface such as file system, key value store, object store and so on.
From now on, I will arrange some part of OpenChannel SSDs : Linux Con Vault 2016
THe usual SSD’s features.
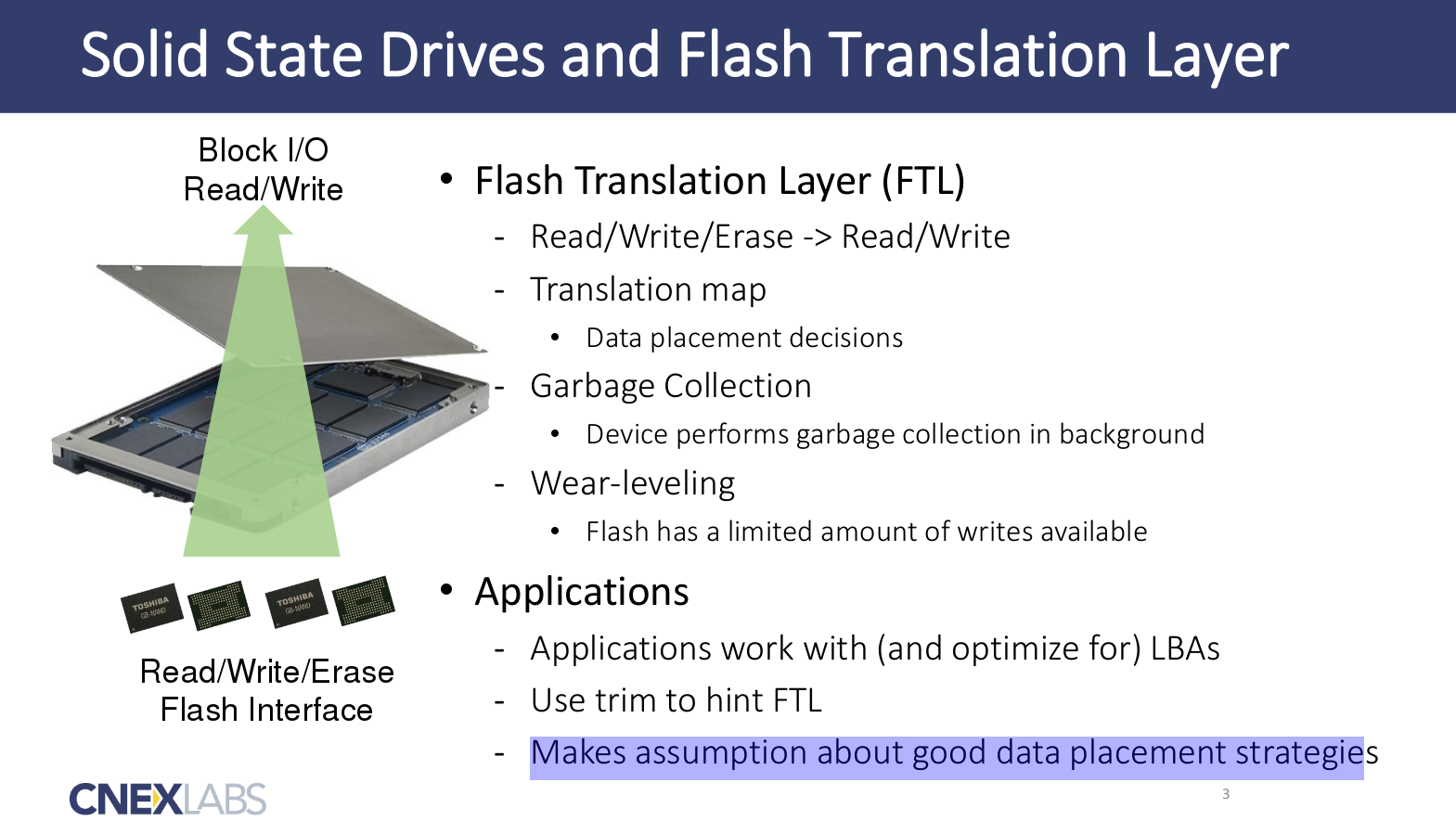
So, typically work inside SSD.
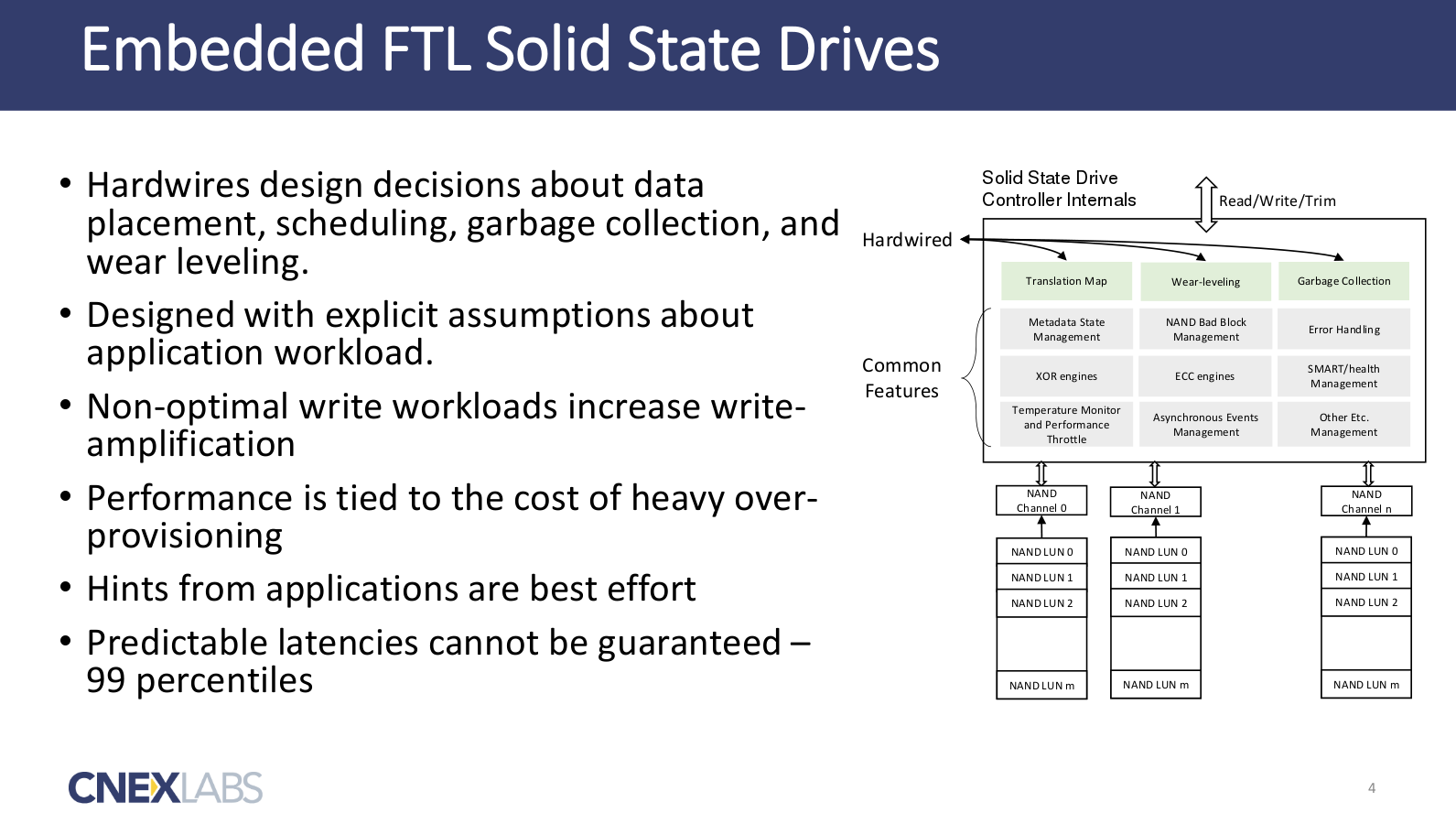
Open-Channel Solid State Drives
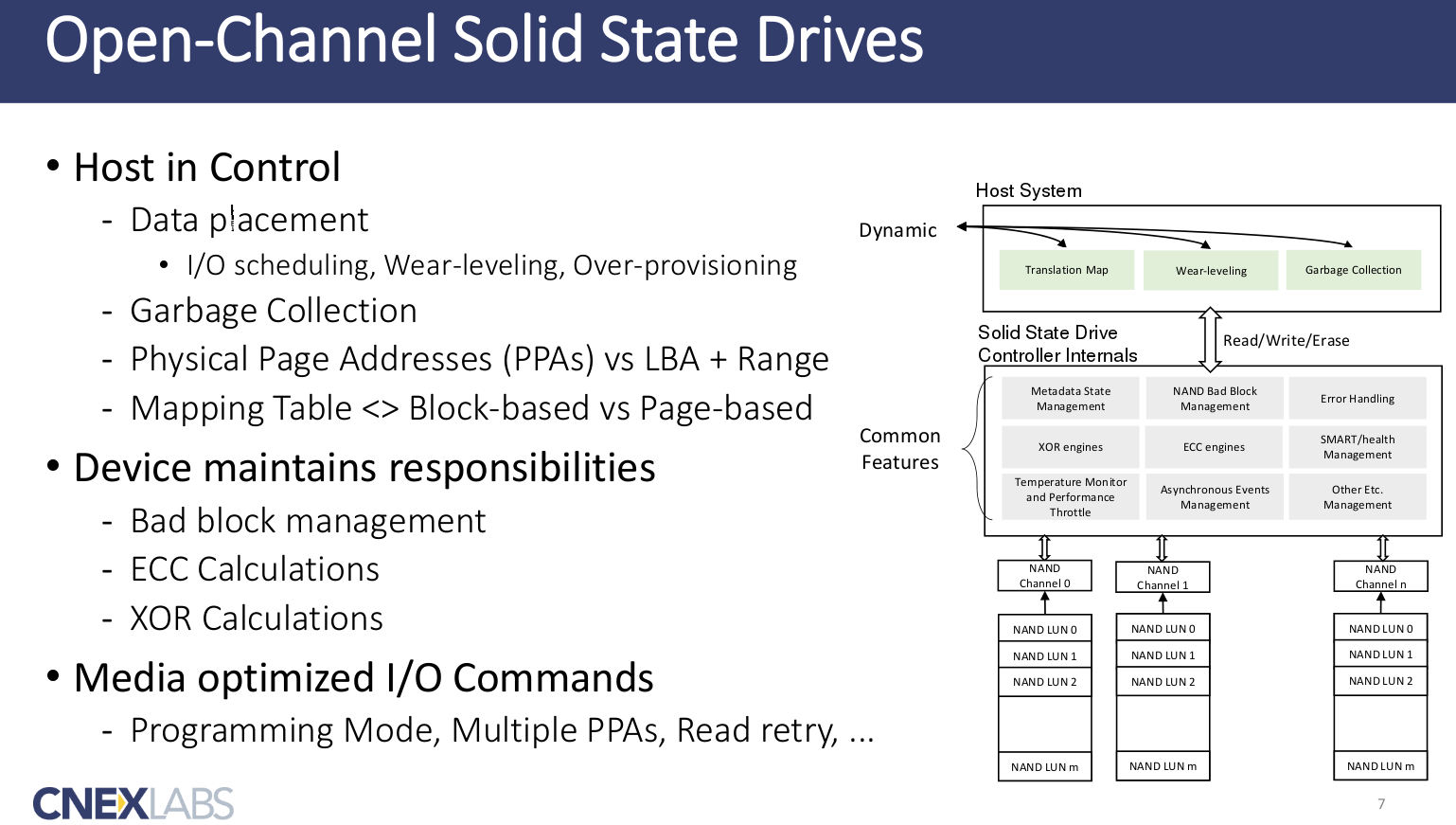
Open-Channel SSD’s new Architecture
Open-Channel SSD’s Specification
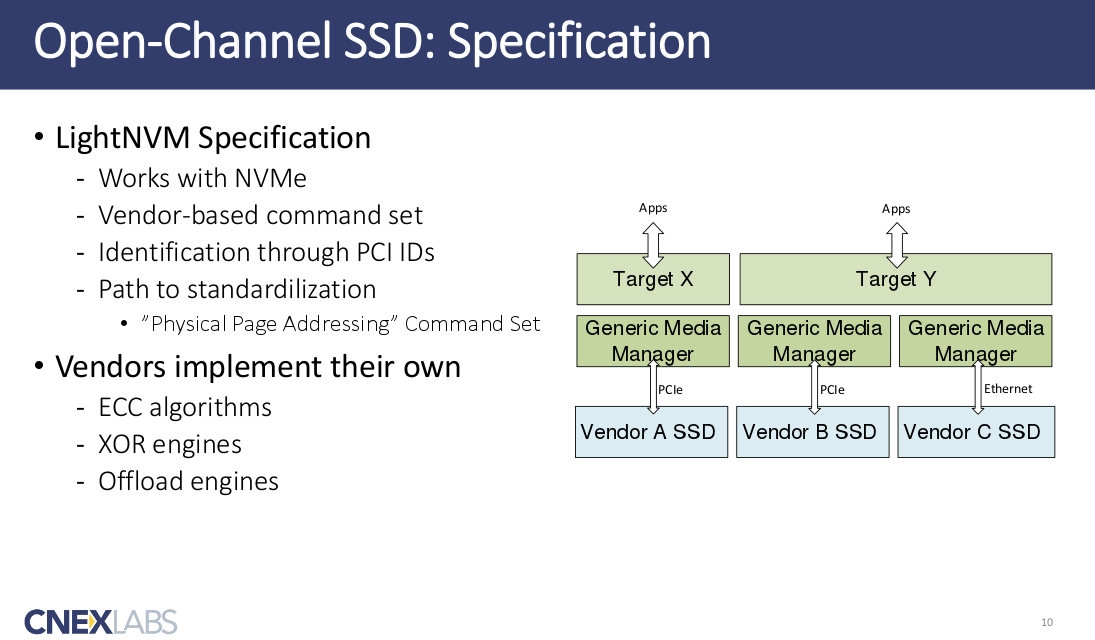
later on, If this version is adopted to mainkernel line.
I will do more detail analysis some page is left on Linux Con Vault 2016.
The following is title of the detailed information in OpenChannel SSDs : Linux Con Vault 2016
-
LightNVM Specification: Identify Command
-
LightNVM Specification: I/O Commands
-
Open-Channel SSD: General Media Manager
-
Open-Channel SSD: pblk target (FTL)
-
Open-Channel SSD: Steady State Example