This post is a brief summary about the paper that I read for my study and curiosity, so I shortly arrange the content of the paper, titled Visual INstruction Tuning (Liu et al. arXiv 2023), that I read and studied.
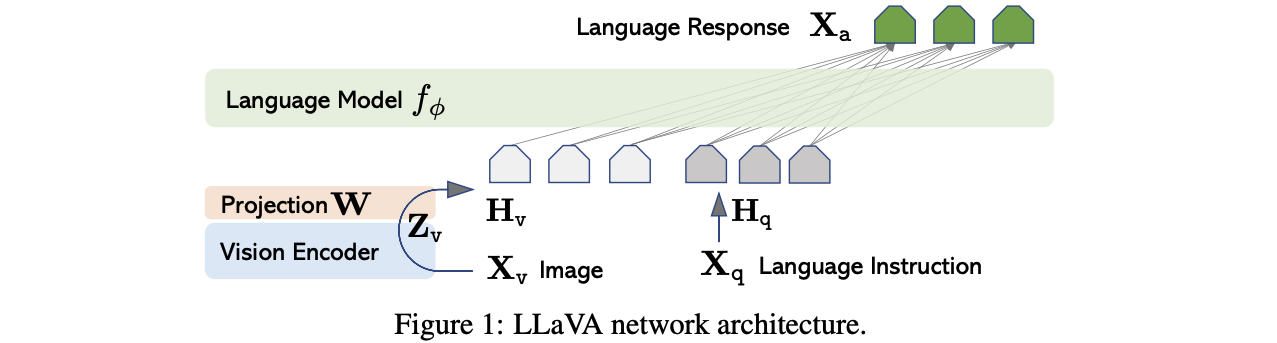

For detailed experiment and explanation, refer to the paper, titled Visual INstruction Tuning (Liu et al. arXiv 2023)
Note(Abstract):
Instruction tuning large language models (LLMs) using machine-generated instruction-following data has improved zero-shot capabilities on new tasks, but the idea is less explored in the multimodal field. In this paper, we present the first attempt to use language-only GPT-4 to generate multimodal language-image instruction-following data. By instruction tuning on such generated data, we introduce LLaVA: Large Language and Vision Assistant, an end-to-end trained large multimodal model that connects a vision encoder and LLM for general-purpose visual and language [this http URL](https://llava-vl.github.io/) early experiments show that LLaVA demonstrates impressive multimodel chat abilities, sometimes exhibiting the behaviors of multimodal GPT-4 on unseen images/instructions, and yields a 85.1% relative score compared with GPT-4 on a synthetic multimodal instruction-following dataset. When fine-tuned on Science QA, the synergy of LLaVA and GPT-4 achieves a new state-of-the-art accuracy of 92.53%. We make GPT-4 generated visual instruction tuning data, our model and code base publicly available.
Reference
- Paper
- For your information
- How to use html for alert
- How to use MathJax