This post is a brief summary about the paper that I read for my study and curiosity, so I shortly arrange the content of the paper, titled A survey on Text-to-SQL Parsing: Concepts, Methods, and Future Directions (Qin et al., arXiv 2022), that I read and studied.
Recently, the generative model in deep learning have significantly advanced the text2SQL task regarding LLM as mapping function from natural language question to an output SQL query.
This paper provides a comprehensive review on deep learning approaches for text-to-SQL parsing.
This paper presented three points such 1) Whether Text-to-SQL copora is single-turn or multi-turn, 2) pre-trained language model and existing method for text-to-SQL parsing, 3) future and potential challenges for text-to-SQL Parsing.
Futhermore, this paper explained the evaluation metric for Text2SQL.
The text-to-SQL is evaluated by comparing the generated SQL with the ground-truth SQL answer. Concretely, there are two types of evaluation metrics that are used for evaluting the single-turn setting, including exact set match accuracy (EM) and execution accuracy (EX). For the multi-turn setting, question match accuracy (QM) and interaction match accuracy (IM) are commonly employed.
For single-trun text2SQL evaluation
-
Exact Set Match Accuracy (EM) is cacluated with vlaues by comparing the ground-truth SQL query and the predicted SQL query. Both ground-truth query and the predicted SQL query are parsed into normalized data structures which have the following SQL ““SELECT””, ““GROUP BY””, ““WHERE””, ““ORDER BY””, ““KEYWORD”“(including all SQL keywords without column names and operators).
-
Execution Accuracy (EX) is calculated with values by comparing the output results of executing the ground-truth SQL query and the predicted SQL query on the database contents shipped with the test set.
For multi-turn text2SQL evalution
-
Question Match Accuracy (QM) is calculated as the EM score over all questions.
-
Interaction Match Accuracy (IM) is calculated as the EM score over all interactions (question sequences).
The following indicate that corpora for learning and evaluating the text-to-SQL(T2S) parsing system.
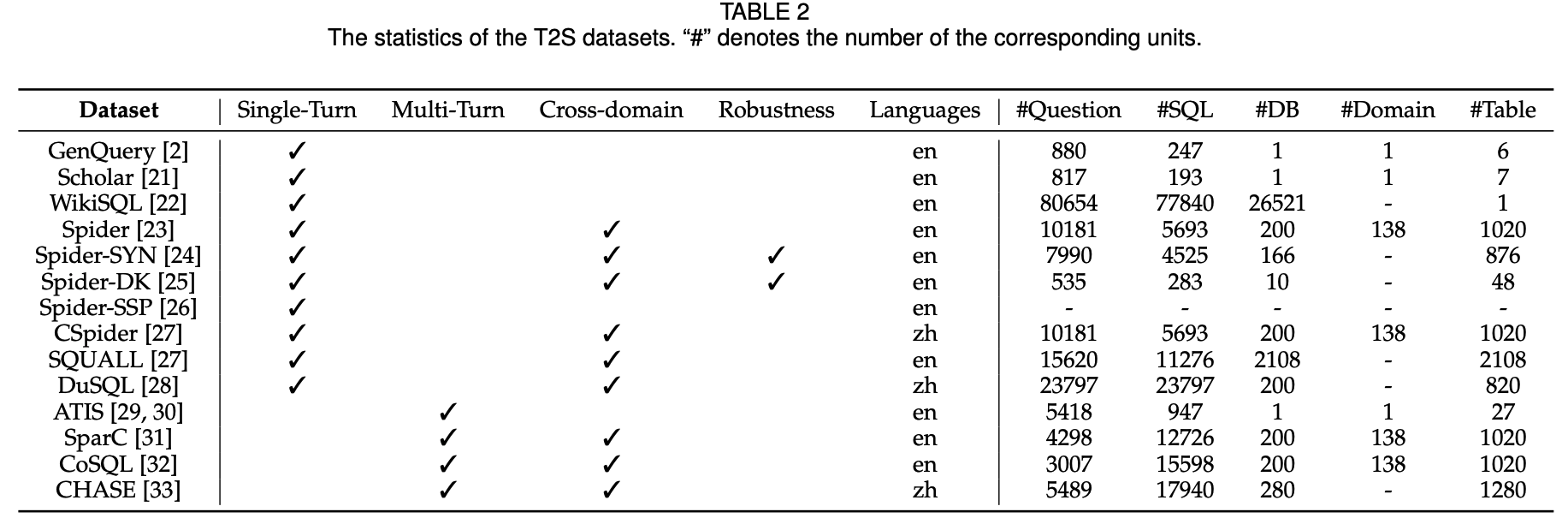
In the figure above, single-turn denotes context-independent & multi-turn is context-dependent. Especially, the SPIDER dataset is widely used on constructing the Text2SQL Parsing system as benchmark.
Deep learing has long been dominant in the field of text-to-SQL parsing, yielding state-of-the-art performances. The following provide a comprehensive review of recent neural network-based approaches for text-to-SQL parsing.
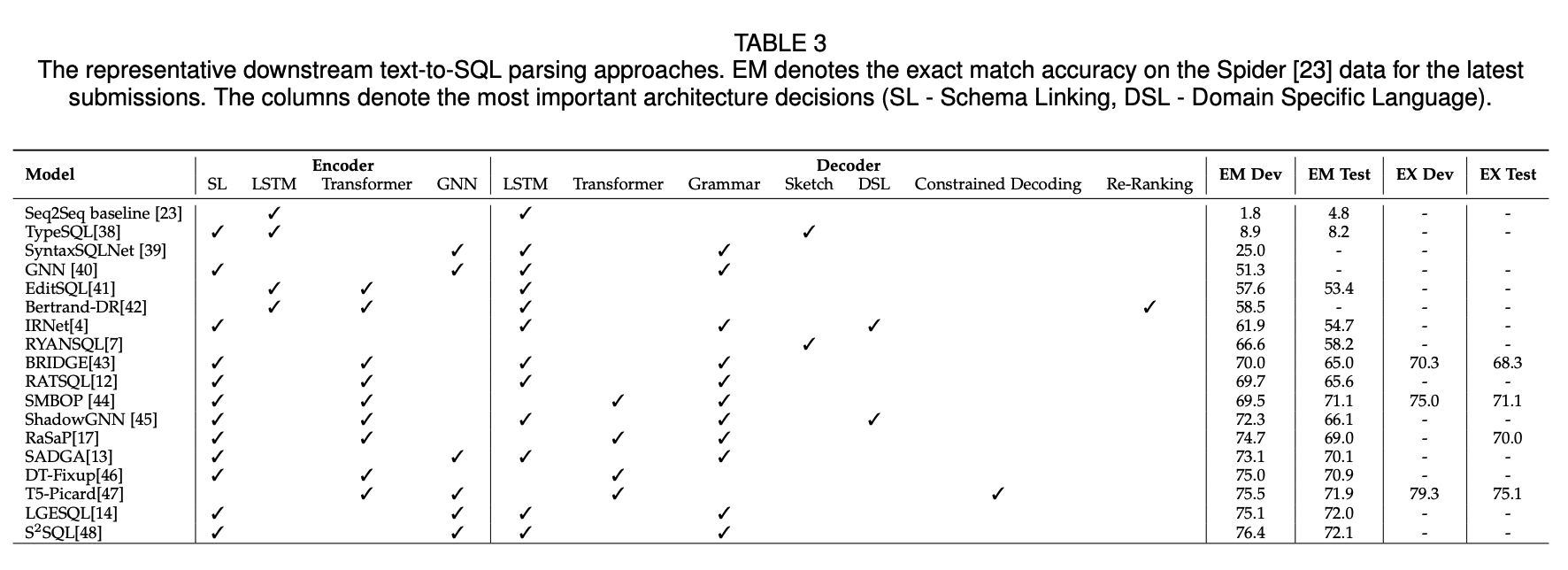
For Text2SQL modeling, Sequence-to-sequence model has widely used in the Text2SQL parsing system.
The follwoing figure 2 explained that encoder should be able to recognize linking structure, schema structure, question structure.
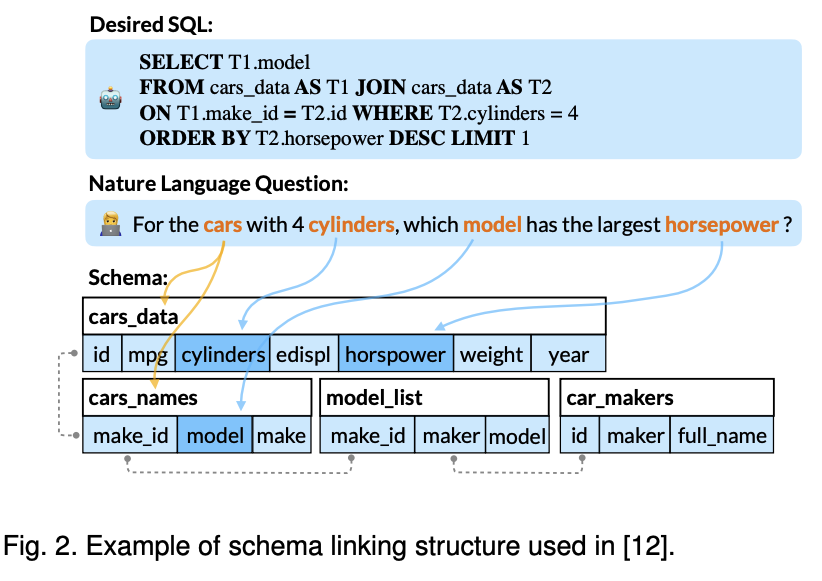
First of all, the linking structure is schema linking which is to identifying references of columns, tables, and condition values in text. In other words, text2SQL parser should learn to detect table or column names mentioned in text by matching question tokens with schema.
The following figure explained the decoder used in exiting Text-to-SQL parsing models can be divided into two categories: sketch-based methods and generation-based methods.
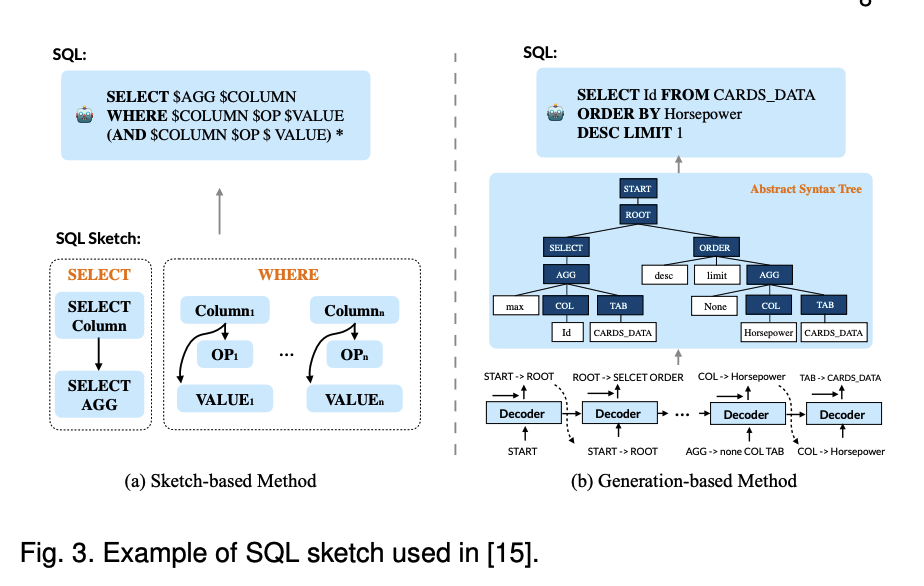
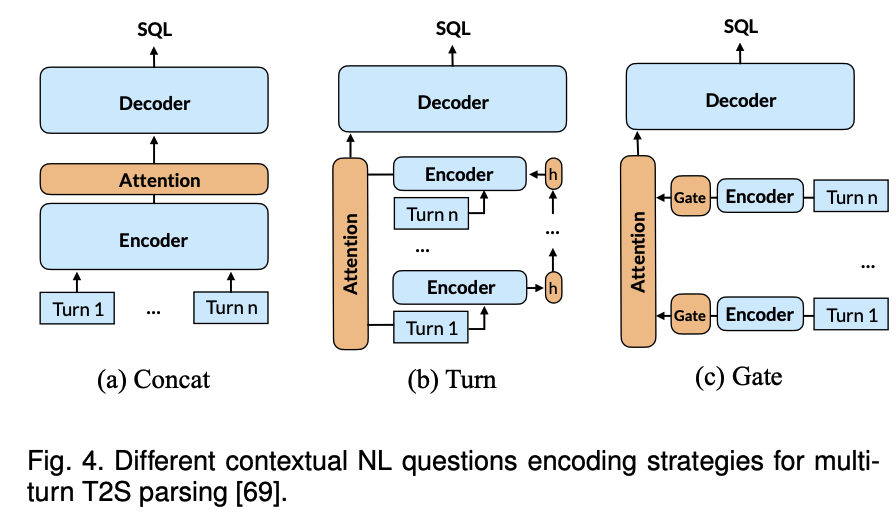
The following how to leverage contextual information in text2SQL Parsing system. Especially, the following indicates how to learning the multi-turn input representation.
Asid from learning the multi-turn input representation, decouples the multi-turn text2SQL parsing into two pipeline tasks which are question rewrting (QR) and single-turn text2SQL parsing.
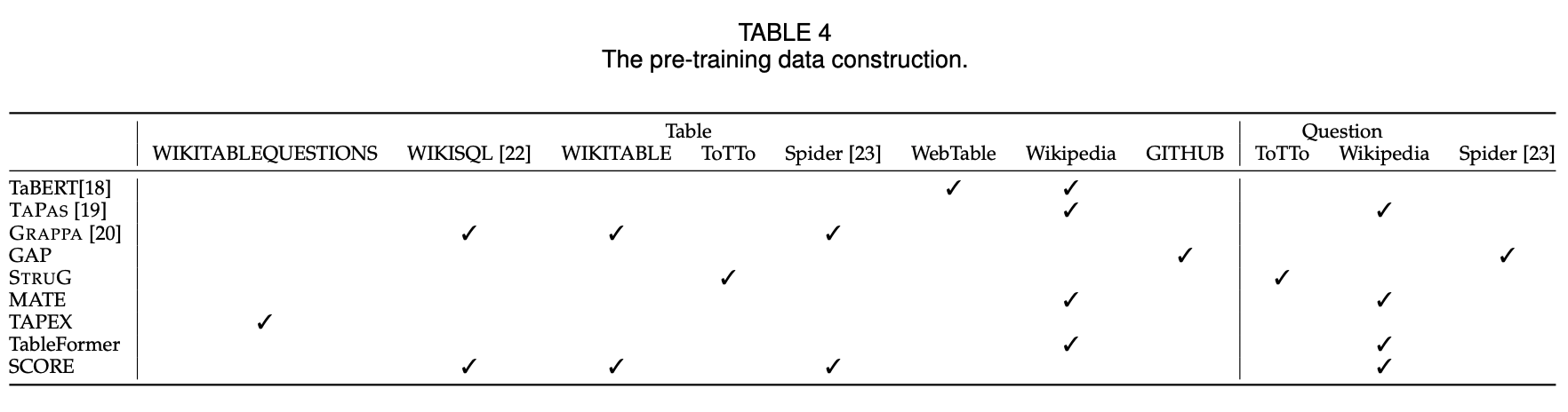
So far, they focus on the text2SQL parsing modeling, The following indicates pre-training data construction for text2SQL parsing tasks.
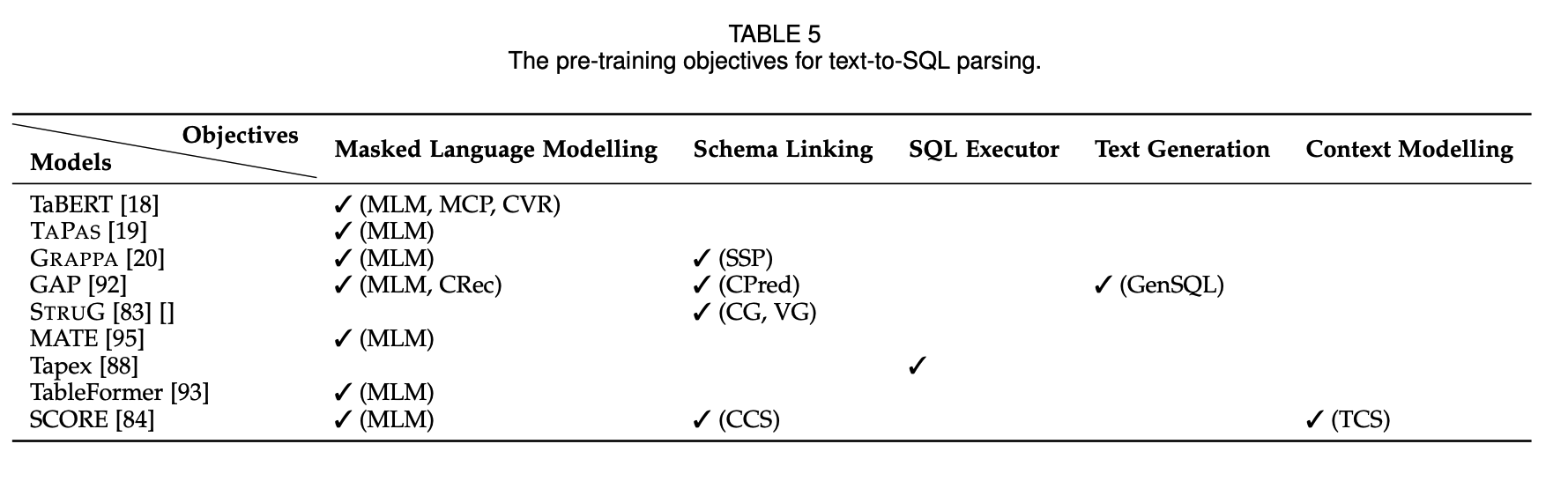
The following is the pre-training objective for text-to-SQL parsing.
For detailed explanation, refer to the paper, titled A survey on Text-to-SQL Parsing: Concepts, Methods, and Future Directions (Qin et al., arXiv 2022)
The paper: A Surevey on Text-to-SQL Parsing: Concepts, Methods, and Future Directions (Qin et al., arXiv 2022)
Reference
- Paper
- How to use html for alert
- How to use MathJax