GCC Practice
A program can be split up into multiple files. This makse it easier to edit and understand, especialy in the case of large. i.e. It also allows the individual pfiles to be compiled independantly.
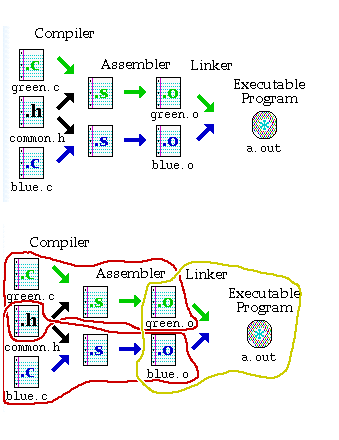
As you can see image above, you can compile source files into object file with -c flag without linking. i.e. the -c flag tells the complier to stop after compliation phase, without linking like thise:
gcc -c green.c
gcc -c blue.c
Then, you can link your two object files as following
gcc green.o blue.o -o ./executable_file
This is normal case when you get your makefile to complie things separately and link them at the end.
Let’s think of an example of how to complie multiple files.
For now, we have five files, add.c, add.h, main.c, substraction.c, substraction.h, substraction.c
add.c and substraction.c includ each function’s body and signature like this
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
## In a file of add.c
int sum_function(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
## In a file of substraction.c
int substraction_function(int a, int b){
if (a > b) {
return a - b;
}
else {
return b - a;
}
}
and then each header file includes the declaration of each function like this :
1
2
3
4
5
## In a file of add.h
int sum_function(int a, int b);
## In a file of substraction.h
int substraction_function(int a, int b);
As you can see each header file, each header file includes the prototype of the function in each c source file.
In the main.c file case :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#include <stdio.h>
#include "add.h"
#include "substraction.h"
int main(){
int test_a = 2;
int test_b = 3;
int result = 0;
result = sum_function(test_a, test_b);
printf("the result of sum_function : %d\n", result);
result = substraction_function(test_a, test_b);
printf("the result of substraction : %d\n", result);
return 0;
}
As you can see that main.c file include each header file such as add.h and substraction.h.
The declaration is used to make sure that the types of the arguments and return vlue match correctlly between the function call and the function definition.
The main function will print the print statements.
As you already know, The difference between the two forms of the include statement, #include “FILE.h” and **#include
So If you want to compile the total files above such as add.c and substraction.c and main.c, Use the following command:
gcc -Wall main.c sum.c abstraction.c -o ./test
This command would creates only executable file named one_shot
The command above is in one_shot_compiling.sh under GCC practice of calling external c function dir in in the repository of hyunyoung2 Cpython and Cython
In this command above, We use th -o opotion to specify the particular output file you want to make as executable file like test.
Note That the header file “add.h” and “substraction.h” is not specified in the list of files on the command line. The directive #include “add.h” in the source file instructs the compiler to include it automatically at the appropriate points.
Let’s see another way like this
First, you create each object file such as add.o , substraction.o , main.o
Second, link each file to make executable like this :
gcc -Wall -c add.c
gcc -Wall -c substraction.c
gcc -Wall -c main.c
gcc -Wall main.o add.o substraction.o -o ./main_two_ways
When you want to run them above, run the shell script, two_ways_compiling_only_for_object_files_without_main_file.sh under GCC practice of calling external c function dir in the repository of hyunyoung2 Cpython and Cython