this article refers to this URL about 7. controller Architecture.
Controller Architecture
When I read this document of nvme spec 1.2
As you can see in chapter 7, there is sentences in the document.
Except for Fused operations. there are no ordering restrictions for precessing of the commands within or across Submission Queues. Host software should not place commands in the list that may not be re-ordered arbitrarily. Data may or may not be committed to the NNM media in the order that commands ar received.
The following article is cited in chapter 7 from nvme spec 1.2.
host software submits commands of higher priorities to the appropriate Submission Queue. Priorty is associatedt with the submission Queue itself, thus the priority of the command is based on the Submission Queue it is issued through. the controller arbitrates across the Submission Queues based on fairness and priority according to the arbitration scheme specified in section 4.11
May I am supposed to control the seqeunce of command as you can read the above paragraph.
This article explains to me precedure after completion of command in NVM subsytem.
Upon completion of the commands byt the NVM subsytem, the controller presents completion queue etries to the host through the appropriate Completion Queues. If MSI-X or multiple message MSI is in use, then the interrupt vector indicates the Completion Queue(s) with possible new Command completions for ths host to process. If pin-based or single message MSI I interrupts are used. Host software interrogates the Completion Queue(s) for new completion queue entries. The host updates the CQ head doorbell register to release Completion Queue entries to the controller and clear the associated interrupt.
** depeding on interrupts. for processing completion queue entries
The following is how to iendtify relationship between Submission Queue entries and Completion Queue entries.
There are no ordering restrictrions for completion to the host. Each completion queue entry identifies the Submission Queue identifier and command idnetifier of the associated command. Host software uses this information to correlate the completions with the commands submitted to the submission Queue(s).
The below shows you host guarantee creating Submssion Queue and completion Queue using Admin commands.
Host software is responsible for creating all required Submission and Completion Queues prior to submitting commands to the controller. I/O Submission and Completion Queues are created using Admin Commands defined in section 5.
nvme Spec 1.2
7.2 Command Submission and Completion Mechanism (informative)
I want to know command processing from the above section.
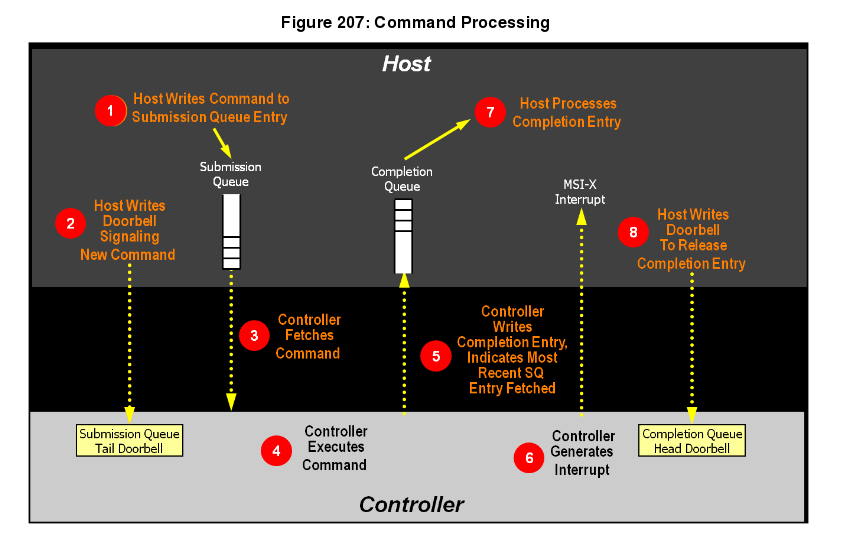
So From now on, I will introduce processing of command about picture on top.
The following article is about Command Processing.
- The host creates a command for execution within the appropriate Submission Queue in memory.
- The host updates the Submission Queue Tail Doorbell register with the new value of the Submission Queue Tail entry pointer. this indicates to the controller that a new command(s) is submitted for processing.
- The Controller fetches the command(s) in the Submission Queue from memory for future execution. Arbitration is the method used to determine the submission queue from which the controller starts processing the next command, refer to section 4.11.
- The controller then proceeds with execution of the next command. Commands may complete out of order.(the order submitted or started execution)
- After the command has completed execution, the controller writes a completion queue entry to the associated Completion Queue. As part of the completion queue entry, the controleer indicates the most recent SQ entry that has been fetched.
- the controller optionally generates an interrupt to the host to indicate that there is a completion queue entry to process. In the above figure, this is shown as an MSI-X interrupt, howerver, it could also be a pin-based or MSI Interrupt. Note that based on interrupt coalescing, an interrupt may or may not be indicated for the command.
- The host processes the completion queue entry in the completion queue, this includes taking any actions based on error condition indicated.
The host writes the Completion Queue Head Doorbell register to indicate that the completion queue entry has been processed. The host may process many entries before updating the associated CQHDBL register.