This article refer to Micron
Write Amplification
Write amplification (WA) is an SSD phenomenon that happens
when the actual amount of written physical data is more than the amount of logical data that is written by host computer.
There are two main factors that cause this difference:
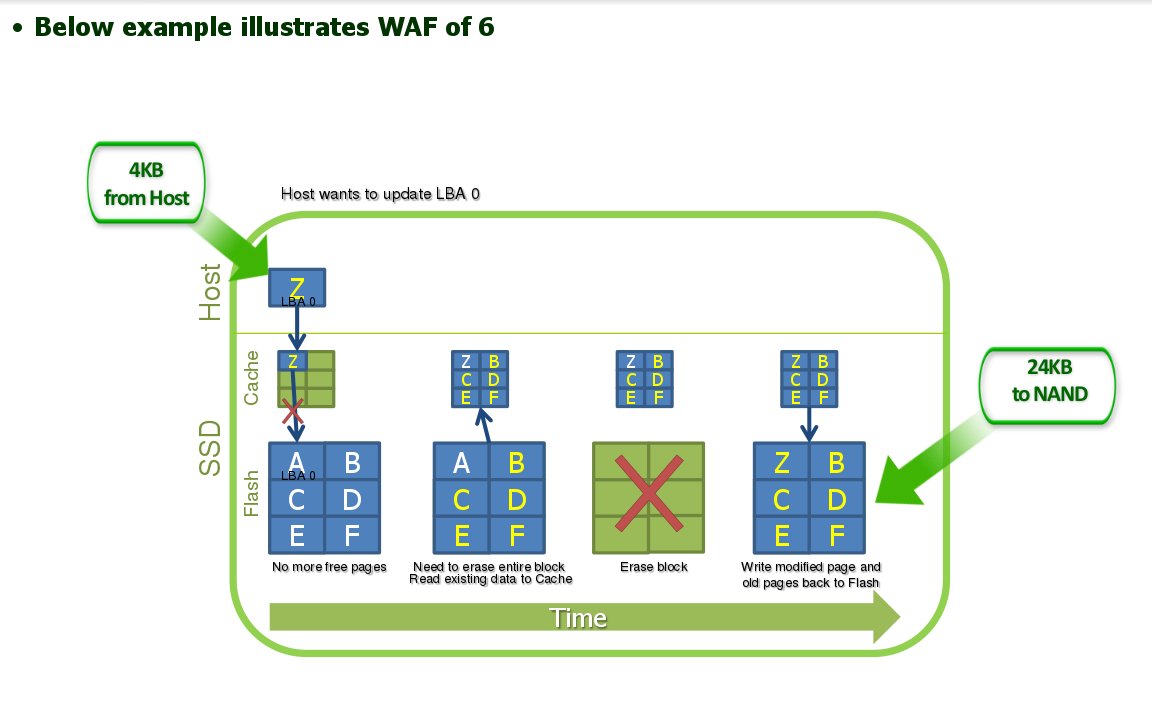
First, every storage device that uses NAND Flash memory is made of elements that must be erased before they can be written.
Second, While NAND flash devices can be written a single at a time. (usually the size of a page is 4K bytes ~ 16 K bytes),
NAND Flash devices can only be erased one block at a time.
a block(also known as a “NAND block” or an “erase block”) can contain hundreds of pages.
This requires the internal movement of saved user data in background operations
That is why the old data in nand frees up adjacent pages of data that are eligible to be erased and available for new data written by the host computer.
Consequently, the total number of actual writes to an SSD is typically more than the number of writes intended to be written by the host computer.
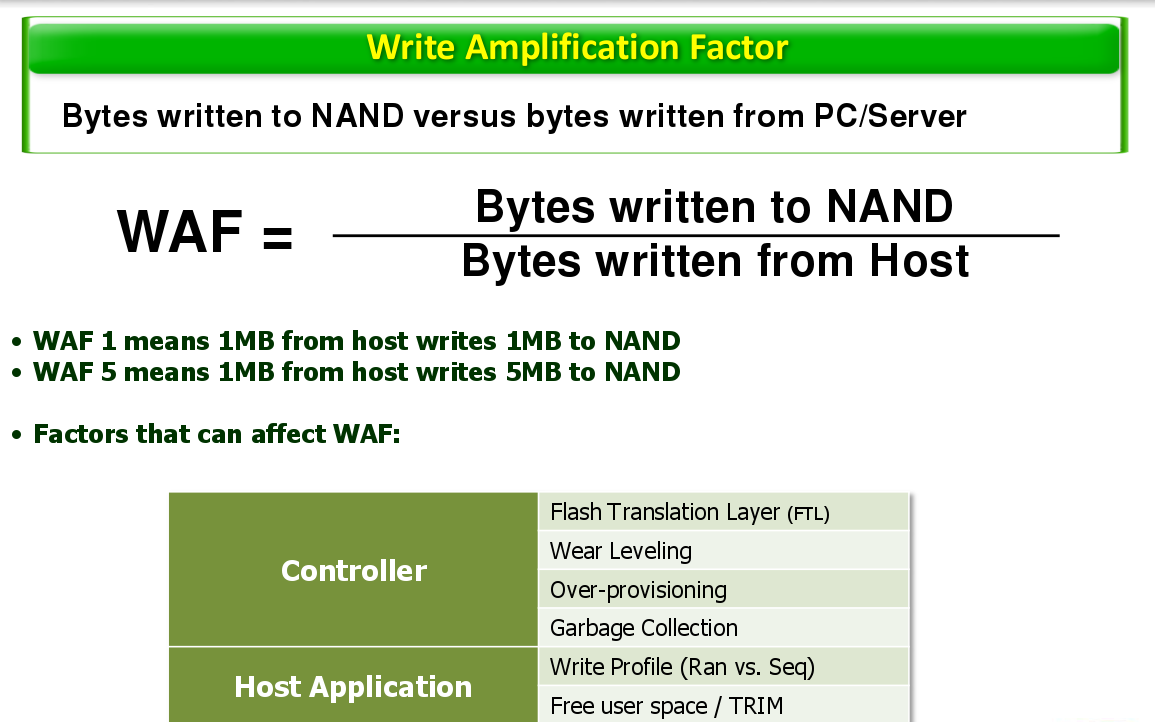
WAF is the mathematical representation of this phenomenon and it describes the ratio of writes to logical writes.
Depending on the nature of the data stream (or workload) from the host computer, Wirte amplification can vary significantly.
Genenrally, small-block random writes will result in a higher WAF and more wear than large-block sequential writes.
Also, full Derives will experience a higher WAF compared to partially-full drrives.
Optimzing workload to minimize WAF can Maximize the lifetime of an SSD.
Calculating the write Amplification Factor
WAF is An Attribute taht tracks the mulitplicative effect of additional writes that result from WA,
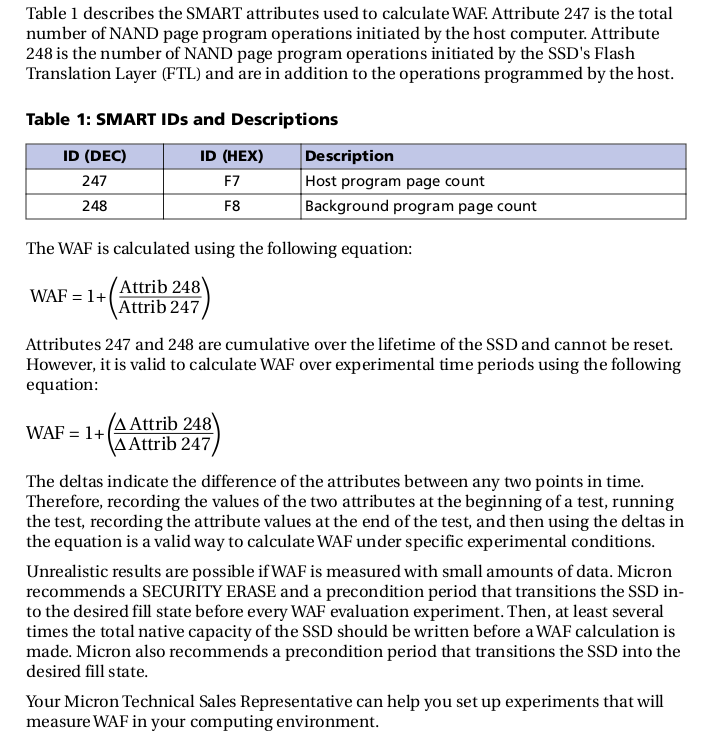
WAF is the ratio of total writes of the NAND divided by the total writes intended by host computer(for example, Linux).
An Ideal WAF would be exactly 1.0.
A WAF that maximizes the lifetime of an SSD would reach 1.0.
The following image is example from Micron
after you want test, IF you want to get to WAF,
you can use the open source nvme-cli with smart attribute.
summarizaiton of WAF
this image is from this URL(SSD)
If you want to calculate WAF, smartdbg command in nvme or smart-log of nvme-cli open-source
So maybe you can calculate WAF with the result of smart-log.
BUT, you need to get another command, especially VU commands to calculate WAF.
And If you want to calculate the precise WAF. you need to fix code of kernel and host side.
BUT If you want WAF value between driver and NAND.
you have to insert code to measure write size.
but that is depending on where starting position is for WAF.
In other words, If you want to get WAF from File system to Nand wit fio tool.
you need two information.
one is the size of file that Fio tool generates, the other is actually information written to nand.
you can get the information written to nand to use smart-log command of nvme-cli.
or You need another command like VU command to get the actual information written to nand.