The previous analysis is brief outline and process of device driver installation and removal.
From now on, I will analyze Blue_DBM in this article.
Let’s start into code of blueDBM driver.
Insmod and rmmod
The Insmod command allows the installation of the module in the kernel.
# insmod nvme.ko
The lsmod command allows you to verify if the module is installed correctly.
# lsmod
# lsmod | grep nvme
The rmmod command allow you to remove the module that you want
# rmmod nvme
If you want to check whether module is removed, Just once again, use lsmod command
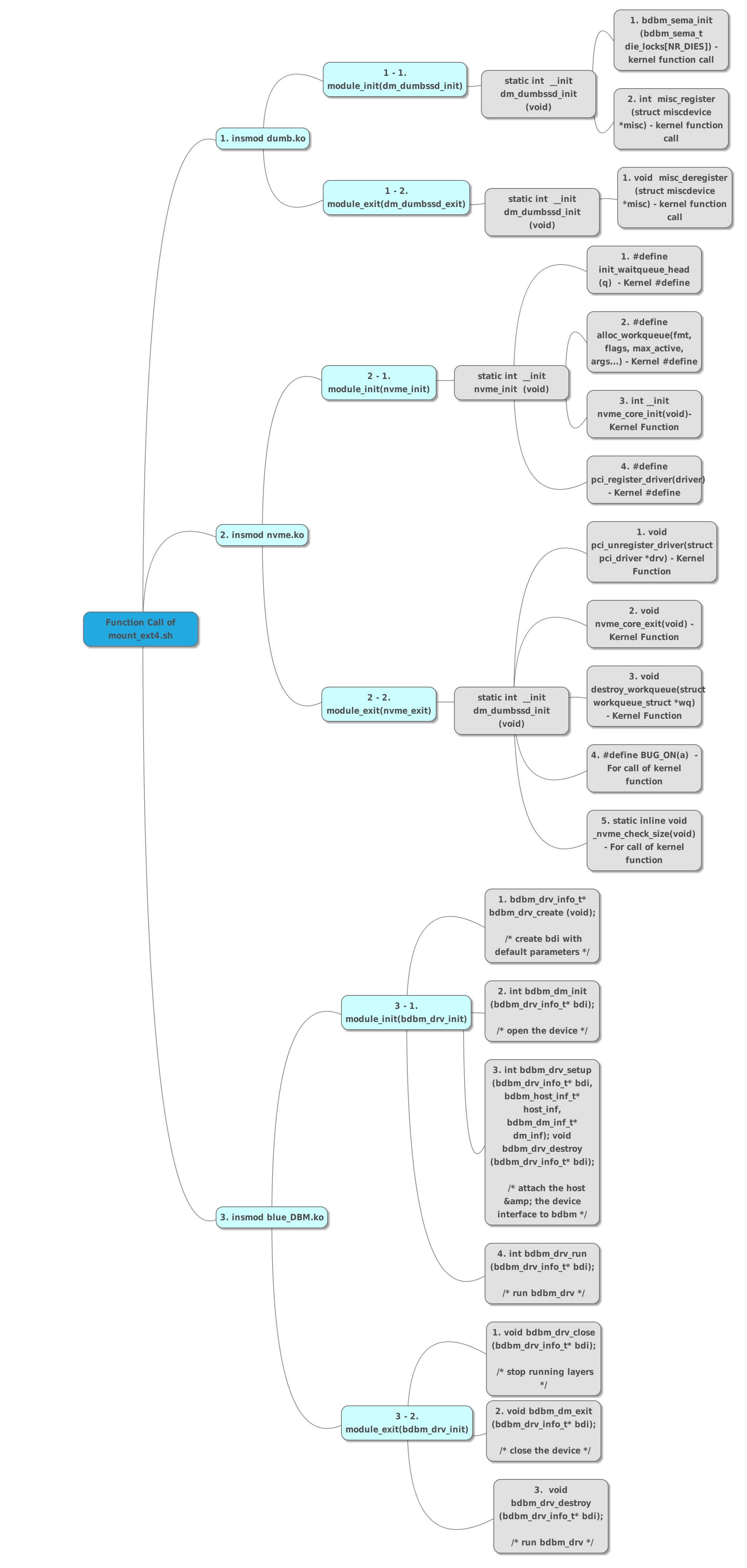
Source tree of mounting Blue_DBM driver.
When you insert module with kernel, You issue insmod, At this time, kernel execute module_init(“name of function for initailization”)
So you have to always look for module_init(“name of function for initailization”), So you can understand to register module.
On the other hand, when you use rmmod command, you have to search for module_exit(“name of function for exit of module”)
At this time you would find flow of exit function of module.
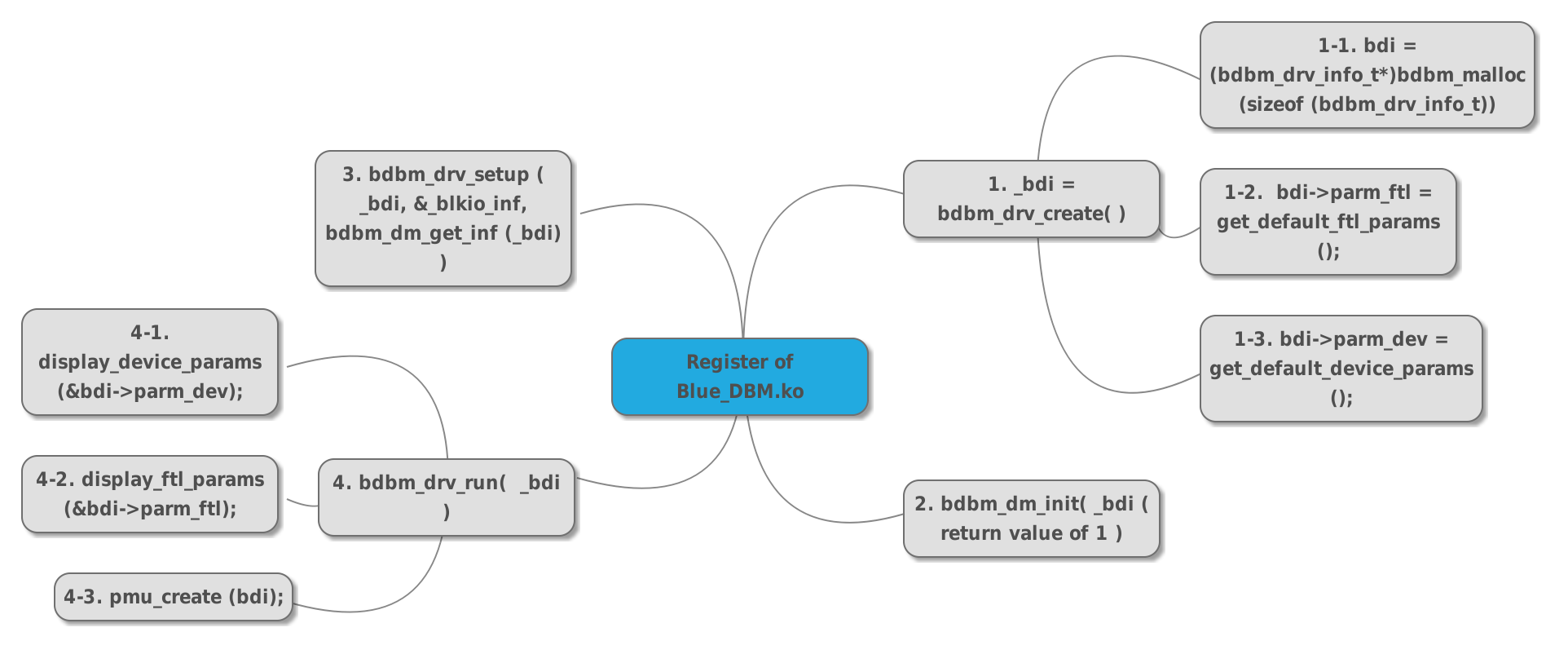
register of Blue_DBM.ko