Sorting.
Now, we check up about a lot of sorting such as bubble, selection, insertion, heap, merge, quick, radix(LSD, MSD) sorting.
bubble sorting
The Sorting is looked like bubble so bubble sorting is siad.
A process of sorting
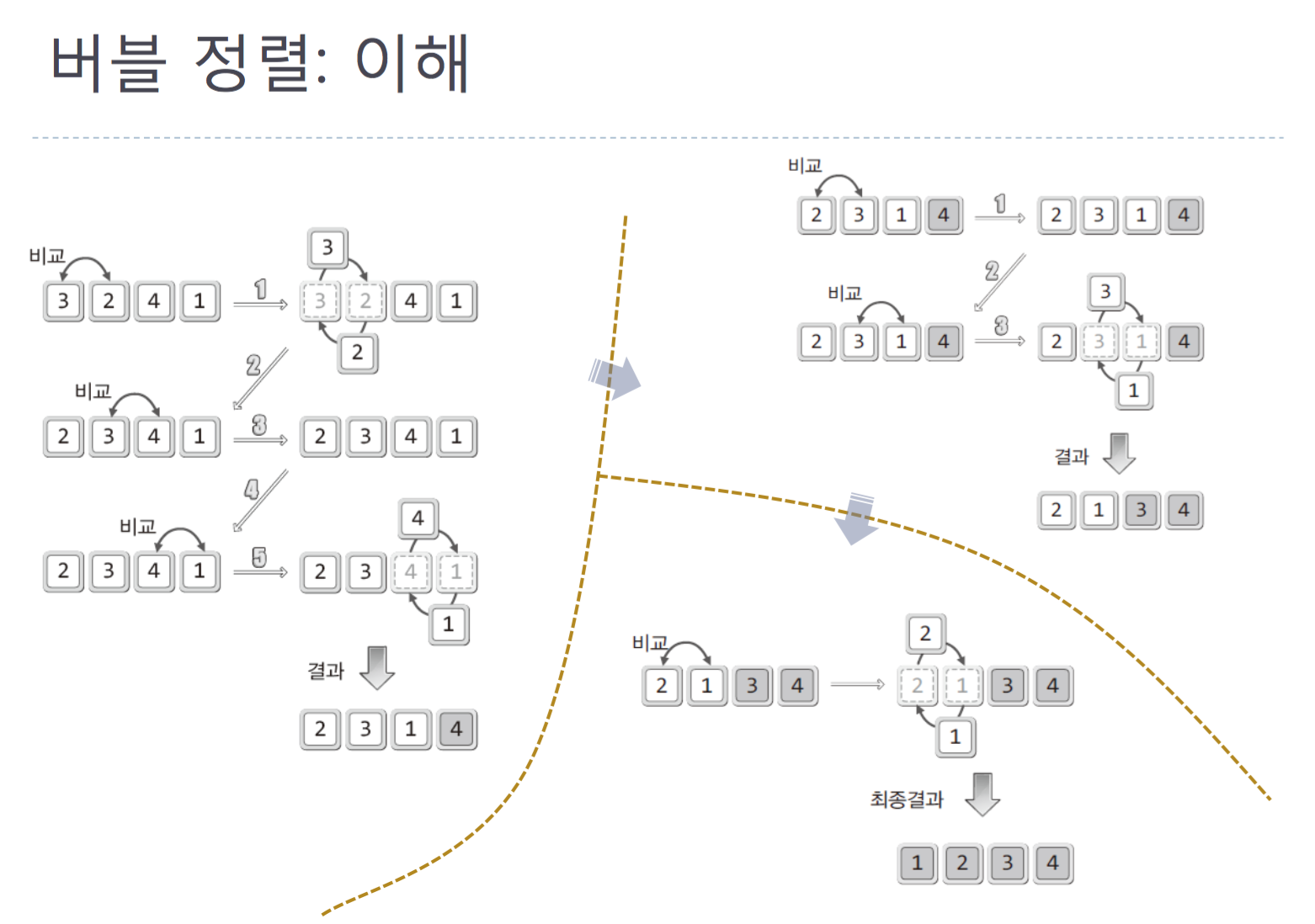
source code of bubble sorting(increase)
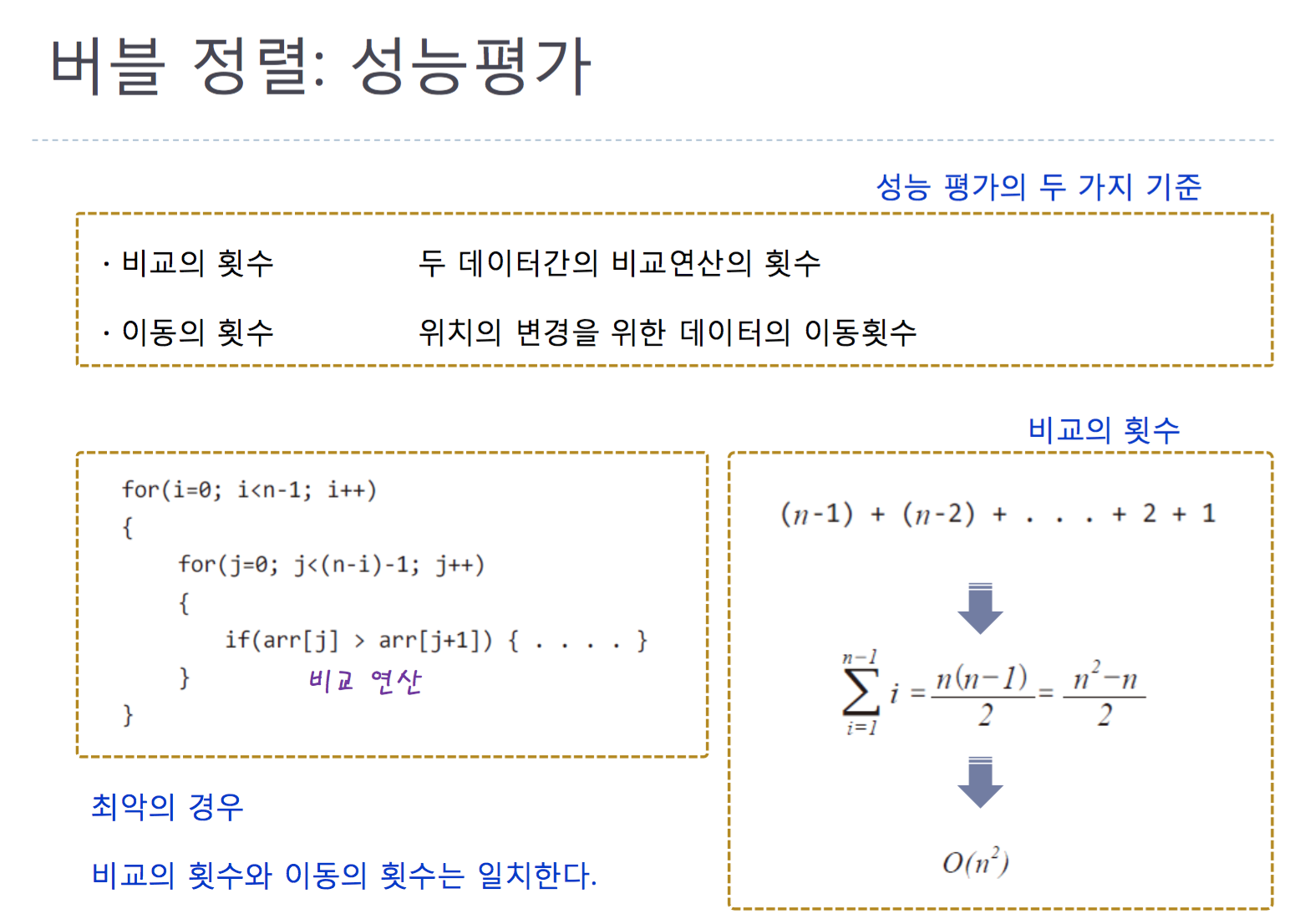
time complexity is O(n^2).
void BubbleSorting(int arr[], int len)
{
int i =0, j=0;
int maxIdx
for(int i = 0 ; i < len-1 ; i++)
{
maxIdx = i;
for(int j = 0 ; j < len - i - i ; j++)
{
if( arr[j] > arr[j+1])
{
int temp = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
Selection Sorting
After seleting the most small value of array, the value lay from front to end.
A process of sorting
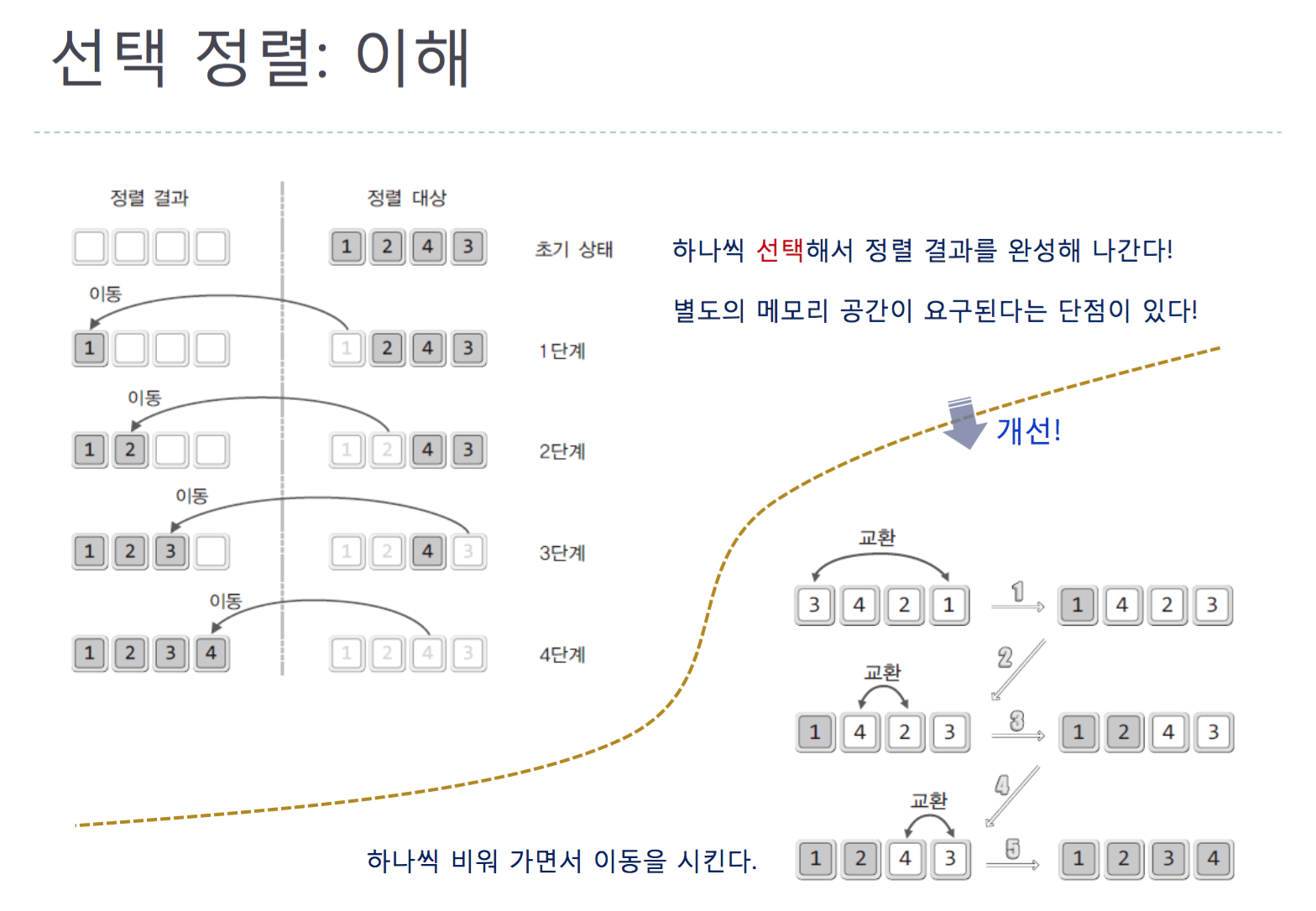
Source code of Selection sorting(increase)
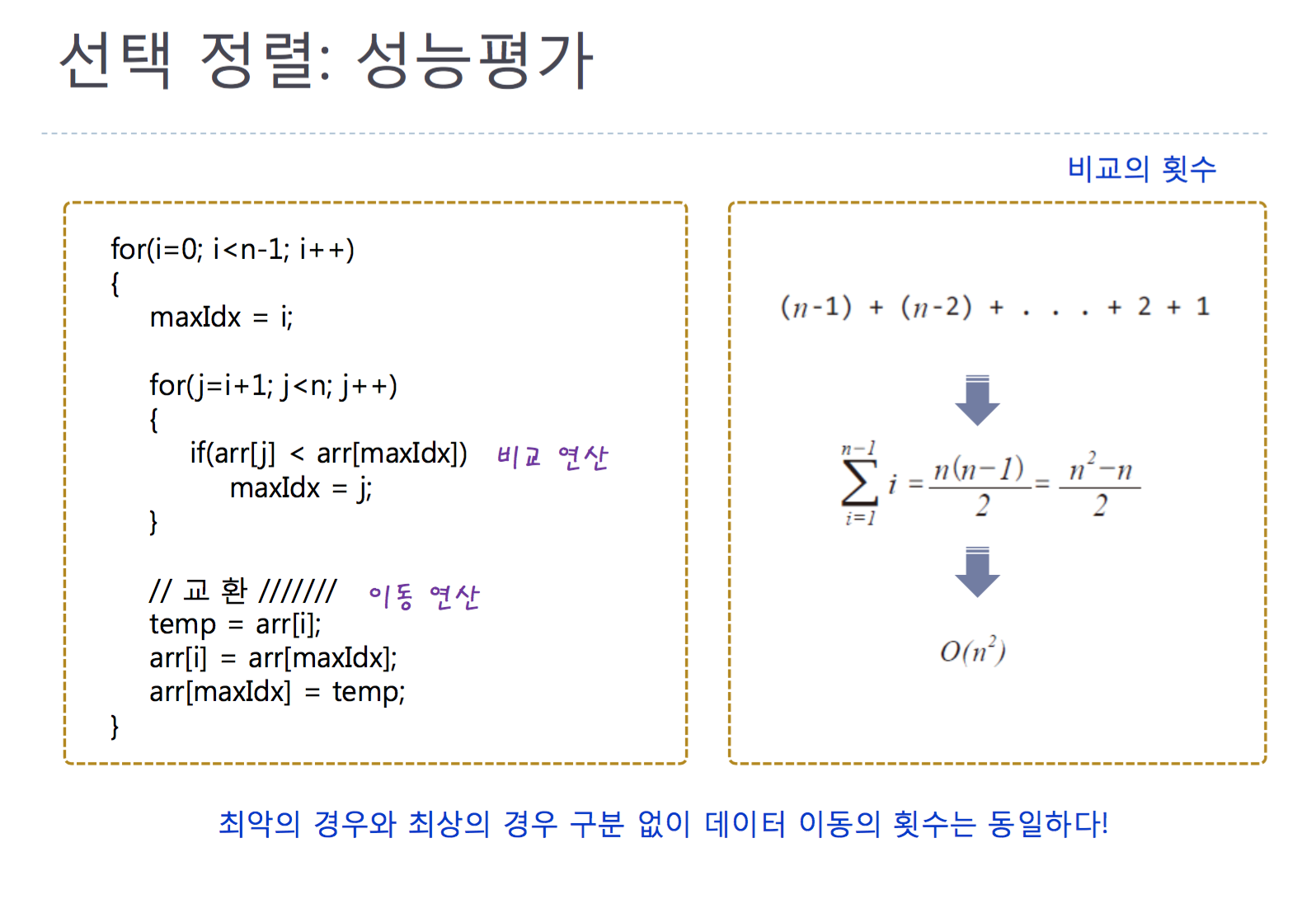
the time complexity is O(n^2).
void SelectionSorting(int arr[], int len)
{
int i =0, j=0;
int maxIdx;
for(int i = 0 ; i < len-1 ; i++)
{
maxIdx = i;
for(int j = i ; j < len ; j++)
{
if( arr[i] > arr[j])
{
maxIdx = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[maxIdx];
arr[maxIdx] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
Insertion Sorting
while the index of array moves from bottom of top, each factor of array is arranged from front.
A process of sorting
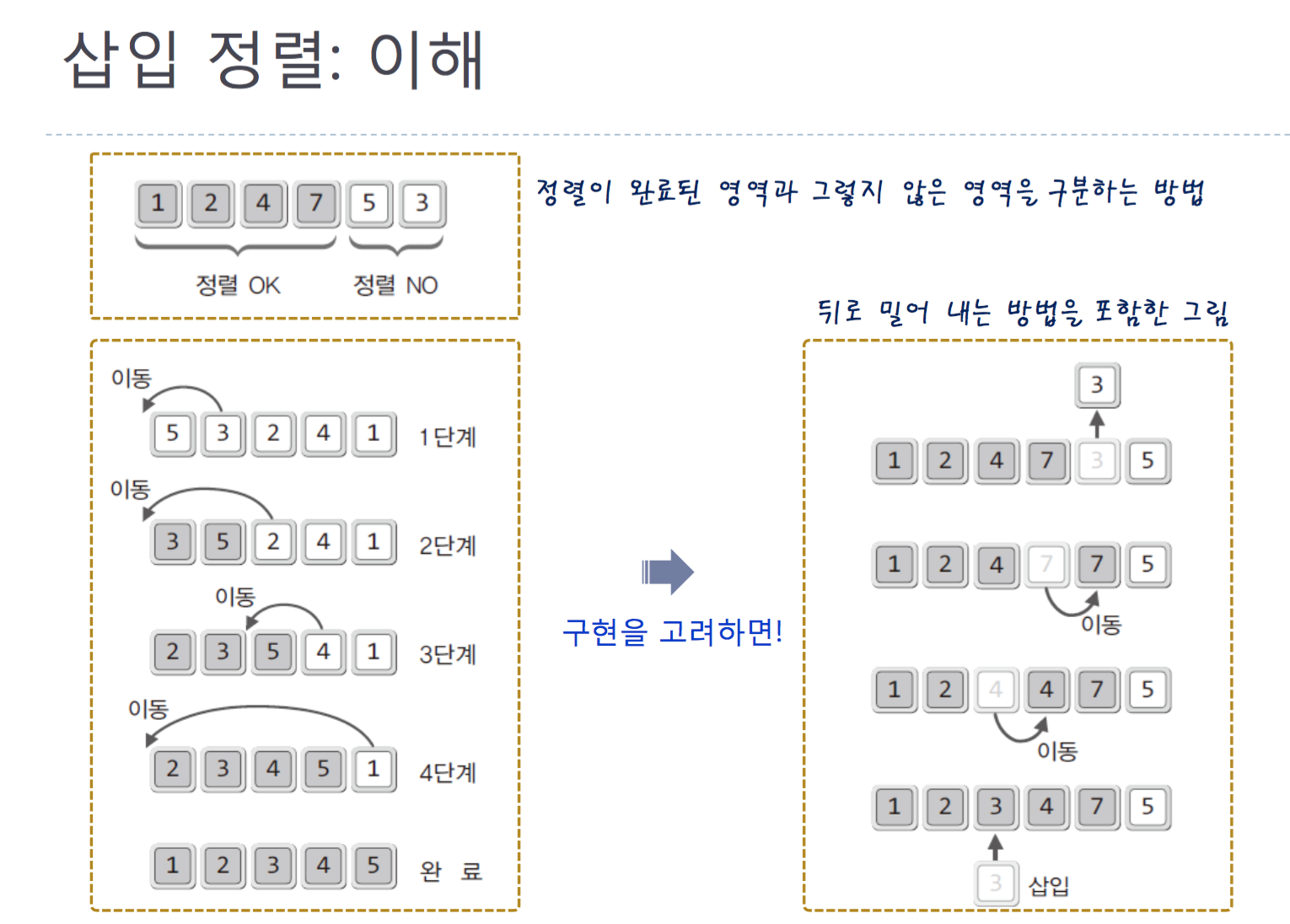
Source code of Insertion sorting(increase)
the time complexity is O(n^2).
void InsertionSorting(int arr[], int len)
{
int i =0, j=0;
for(i = 1 ; i < len ; i++)
{
int temp = arr[i];
for(j = i-1 ; j >= 0 ; j--)
{
if( temp < arr[j])
{
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
}
else
{
arr[j] = temp;
break;
}
}
}
}
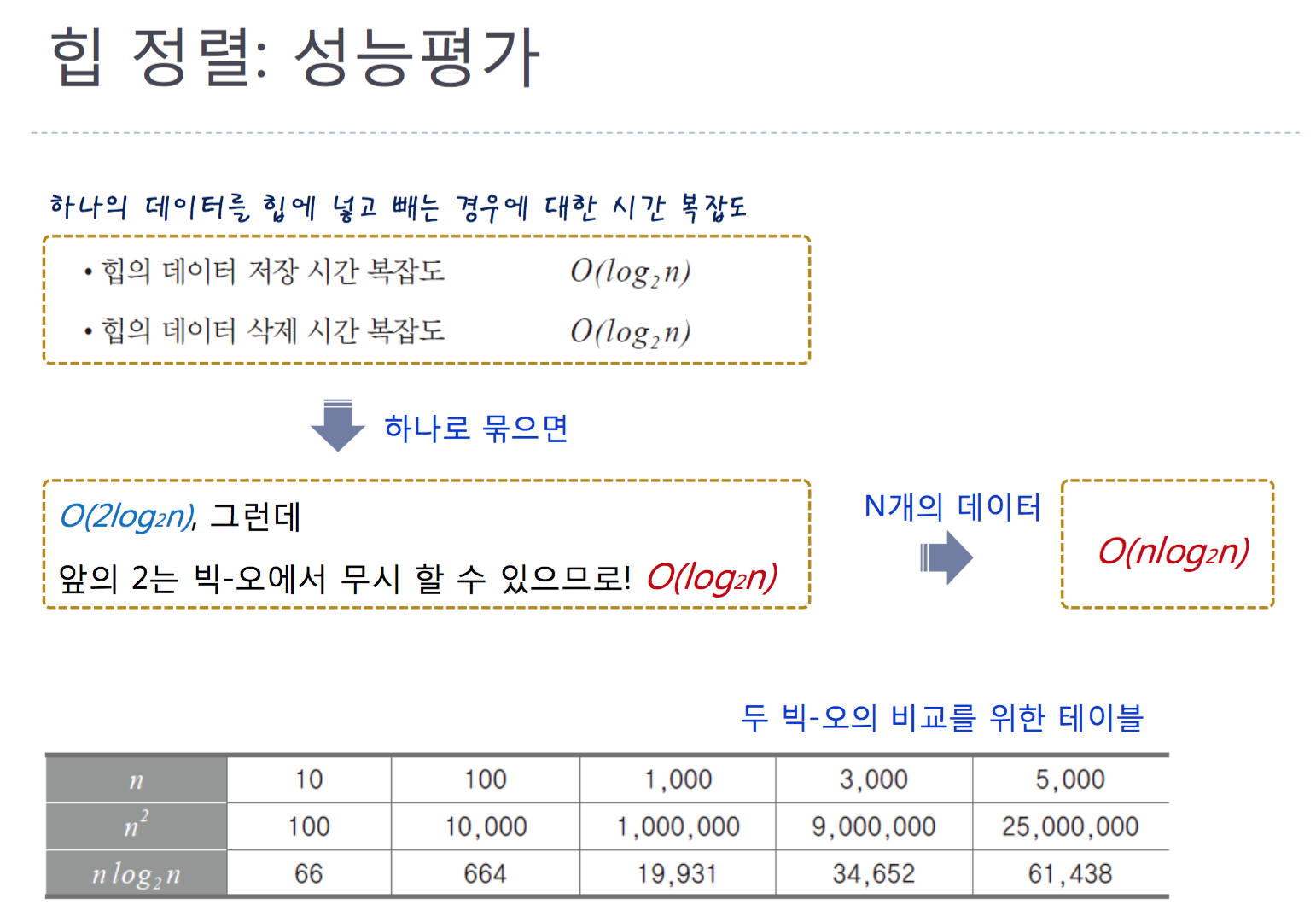
Heap Sorting
This uses heap for sorting. after you insert integers in heap, if You delete data from heap.
data is aligned to from bottome to top.
Source code of heap sorting(increase)
the time complexity is O(nlog N).
The source code below is implemented under making heap.
void heapSorting(int arr[], int len)
{
int i =0;
Heap heap;
for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++)
{
HInsert(&heap, arr[i]);
}
for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++)
{
arr[i] = HDelete(&heap);
}
}
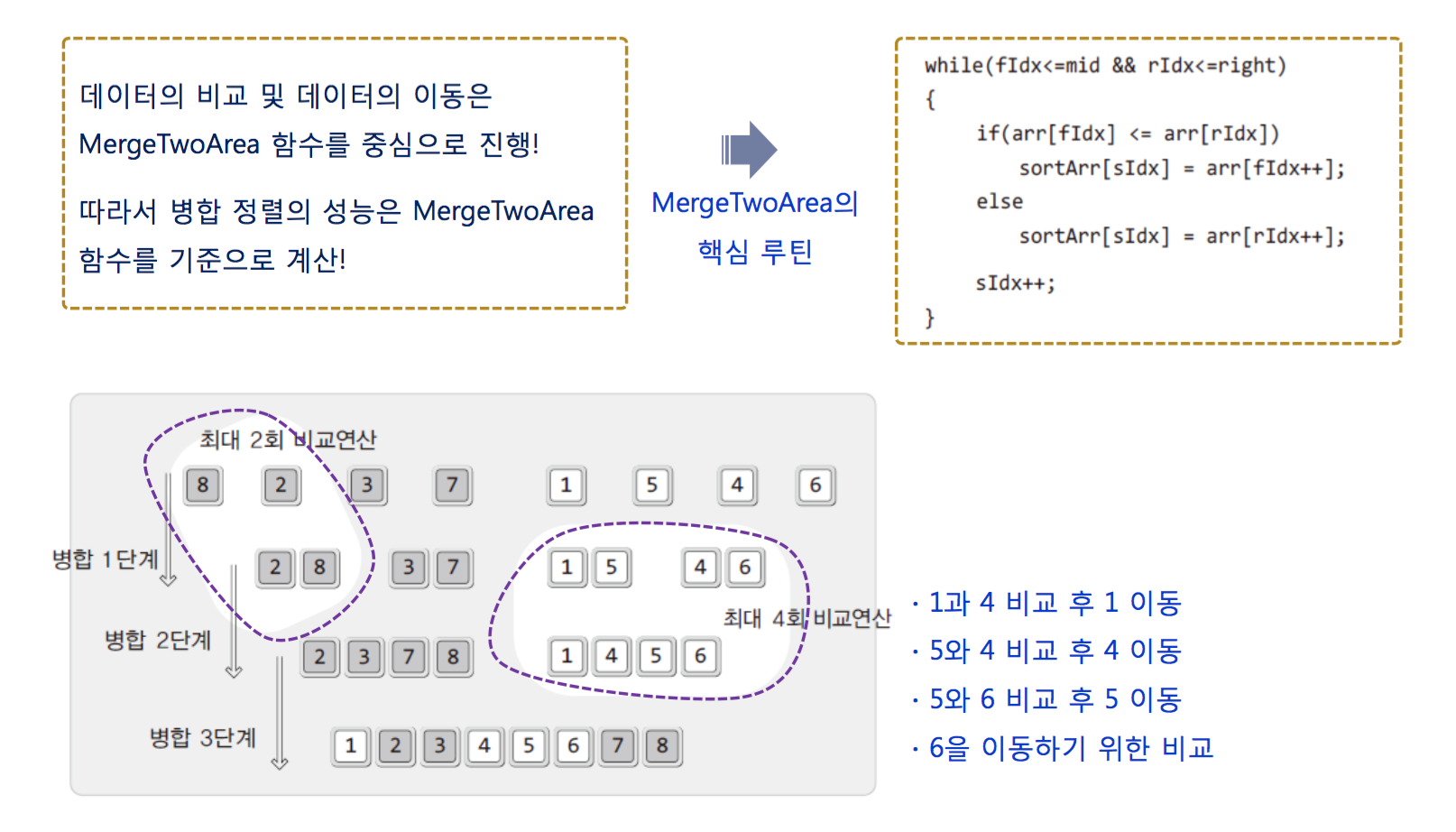
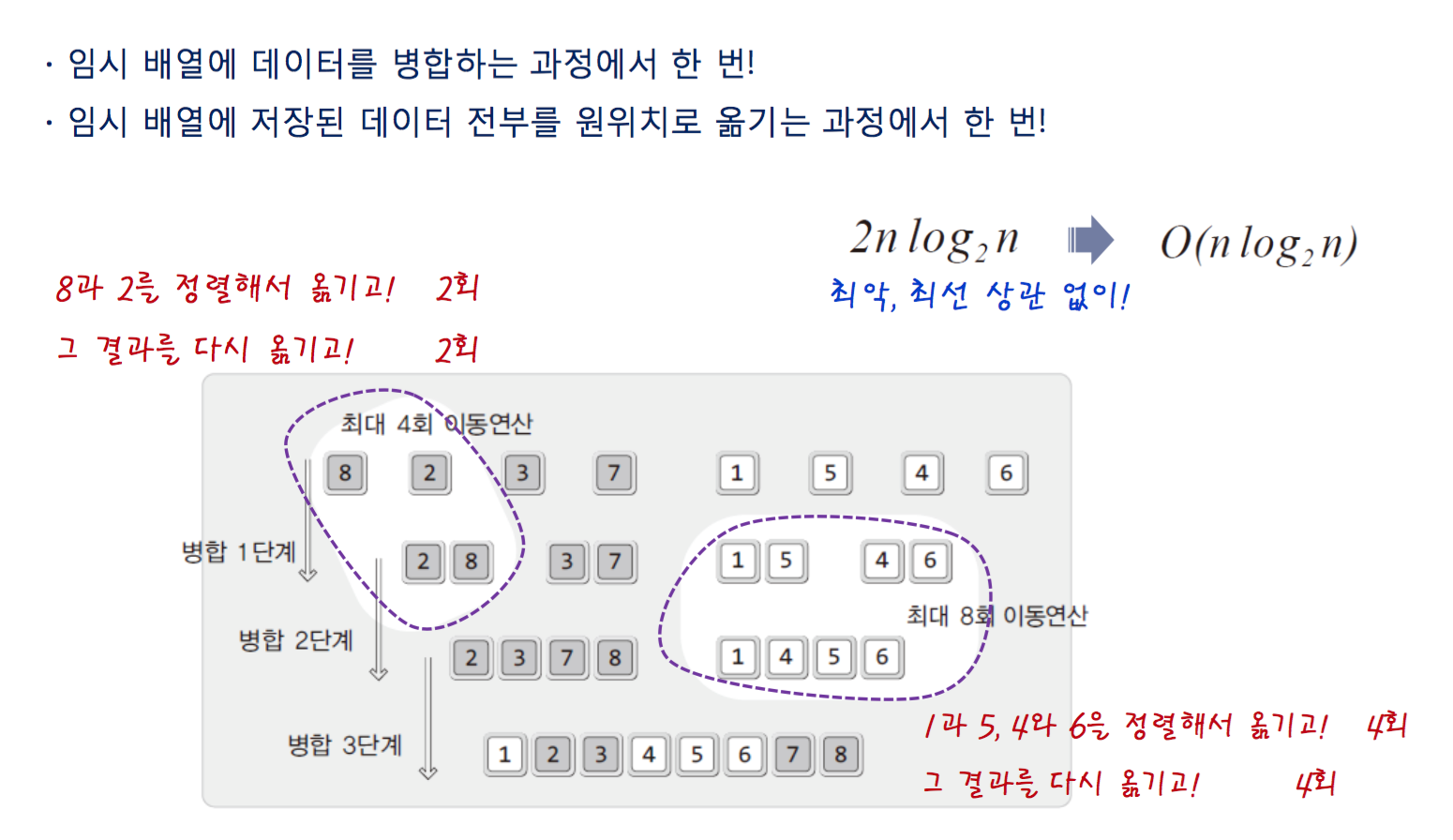
Merge Sorting
Divide and Conquer!! So after you divide the problem into small piece. You solve the problem.
I use the recursvie function.
A process of sorting

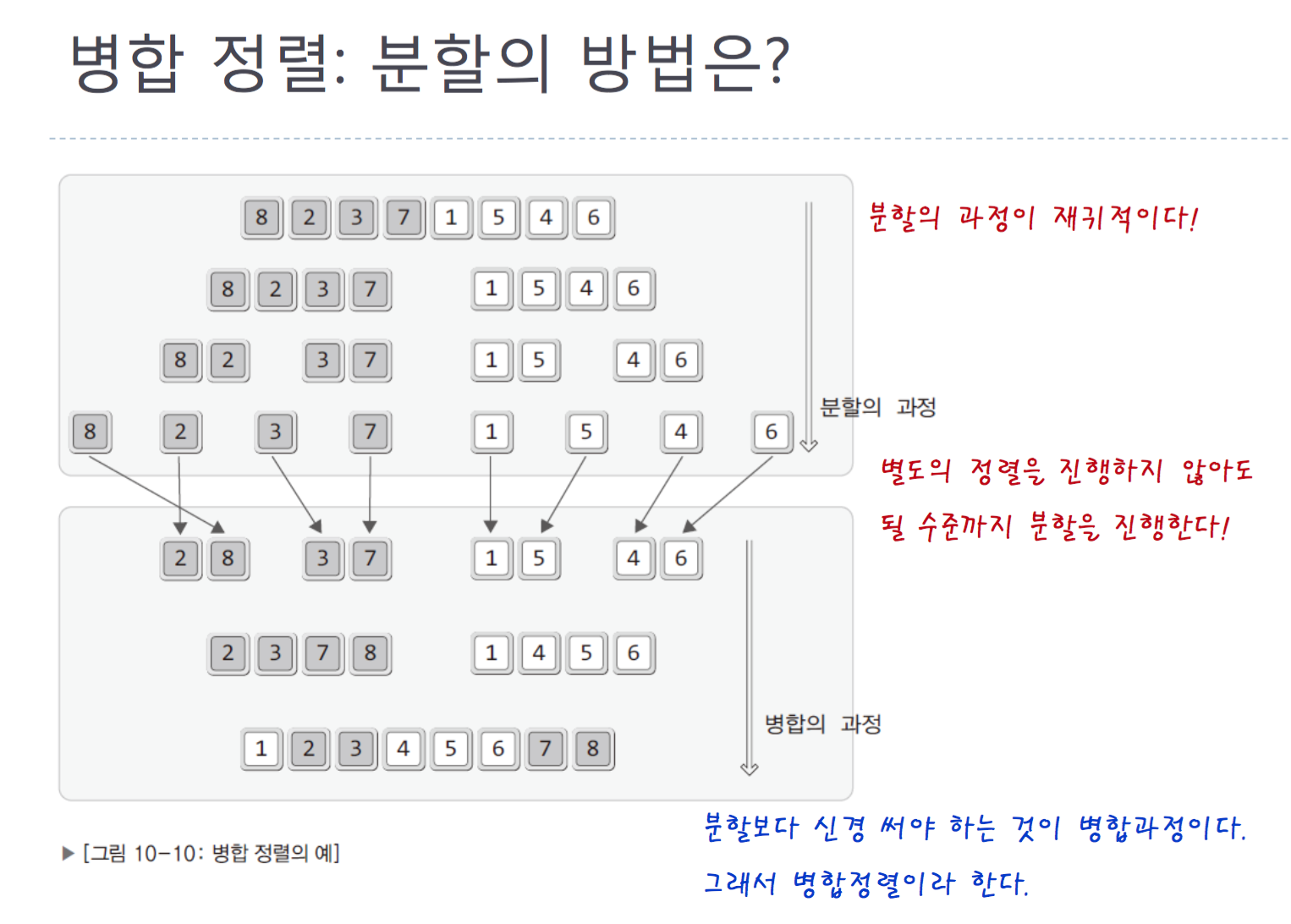
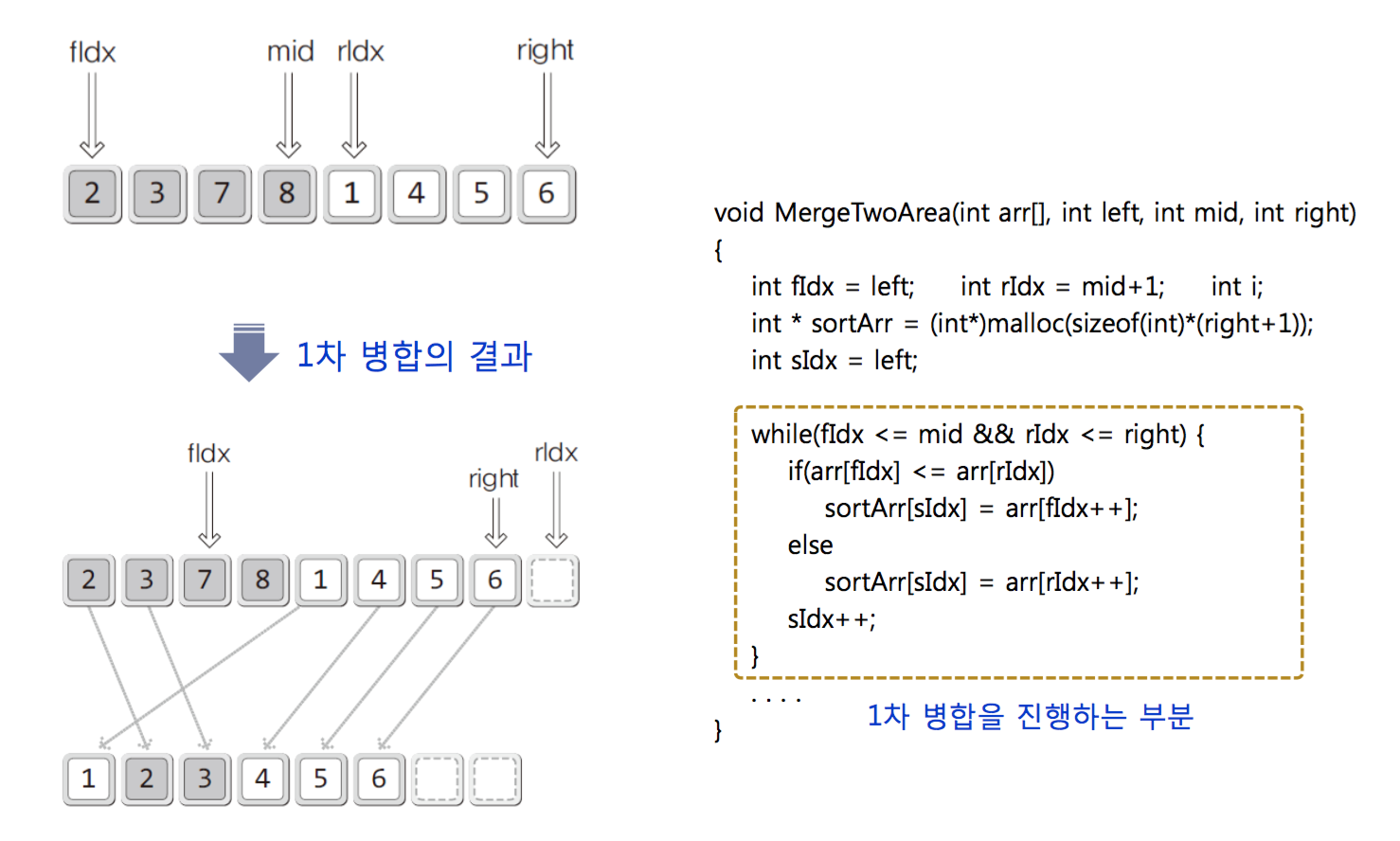
Source code of Merge sorting(increase)
the time complexity is O(nlog N).
First, just Divide the array into half. secode, merging the divied array, you sort array.

void MergeSorting(int arr[], int left, int right)
{
if(left < right)
{
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
/// until array is not divide into half. you continue to divide array.
MergerSorting(arr, left, middle);
MergerSorting(arr, middle+1, right);
MergeTwoArea(arr, left, middle, right);
}
}
void MergeTwoArea(int arr[], left, middle, right)
{
int leftIdx = left, rightIdx = middle+1;
int * copy = (int *)malloc(sizeof(right +1));
int i = 0;
int sIdx = left;
While(leftIdx <= middle && rightIdx <= right)
{
if( arr[leftIdx] <= arr[rightIdx])
copy[sIdx] = arr[leftIdx++];
else
copy[sIdx] = arr[rightIdx++];
sIdx++;
}
if(leftIdx > middle)
{
for( i = rightIdx ; i <= right ; i++, sIdx++)
copy[sIdx]= arr[i];
}
else
{
for(i = leftIdx ; i <= middle ; i++, sIdx++)
copy[sIdx] = arr[i]
}
for(i = left ; i <= right ; i++)
{
arr[i] = copy[i];
}
free(copy);
}
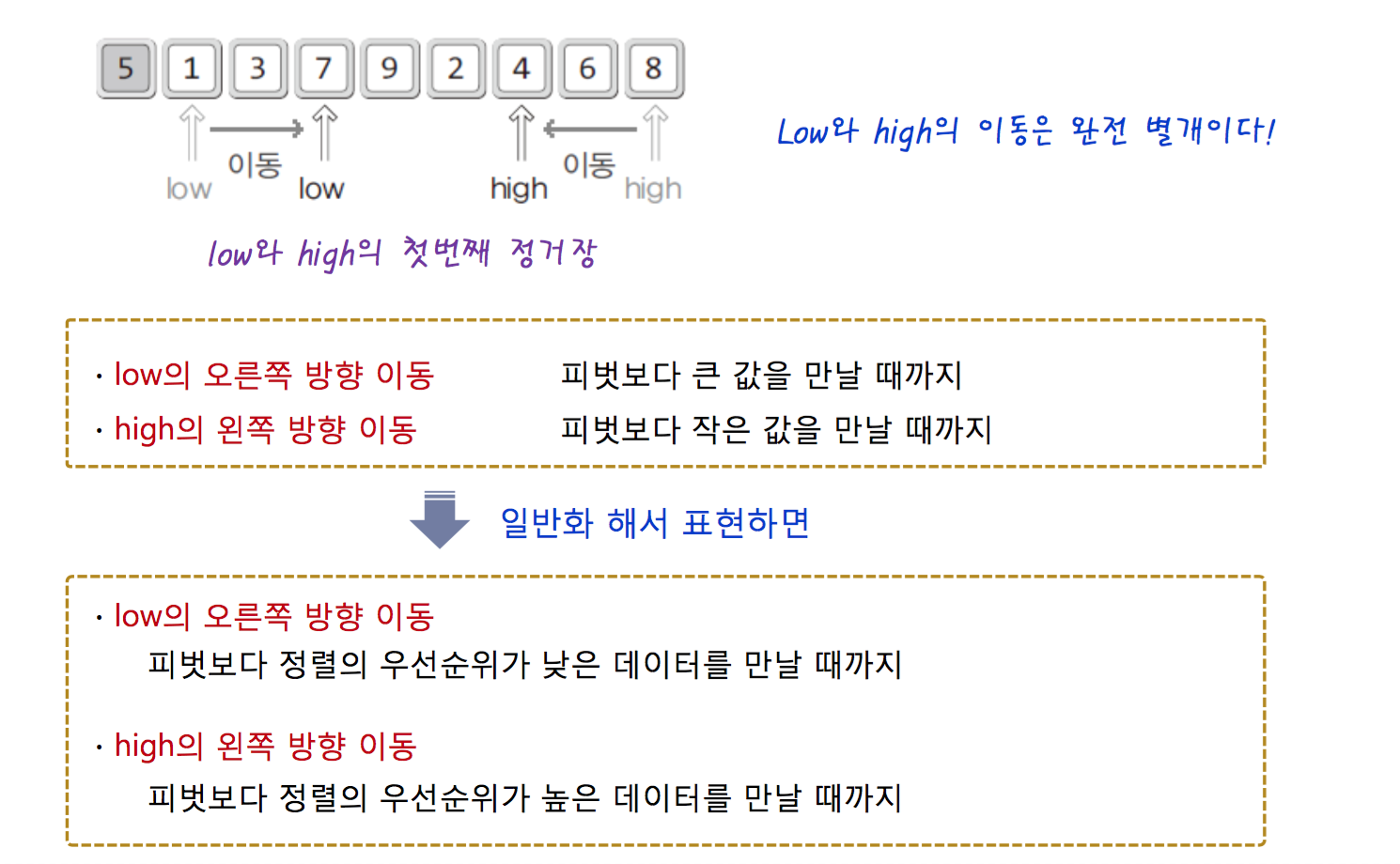
Quick Sorting
This is famous in sorting, so Many people use it.
This sorting uses pivot, so pivot is Important.
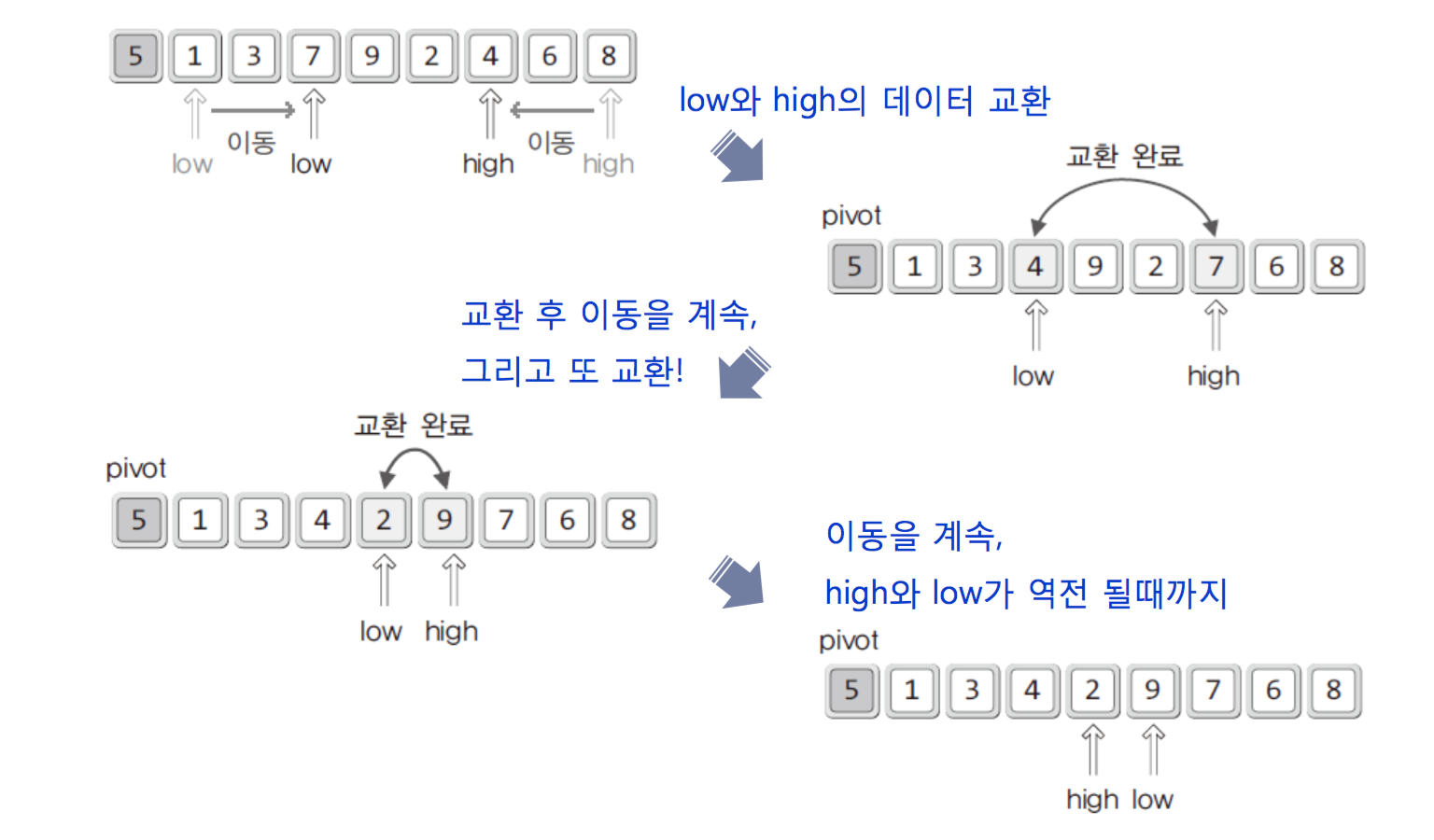
A process of sorting

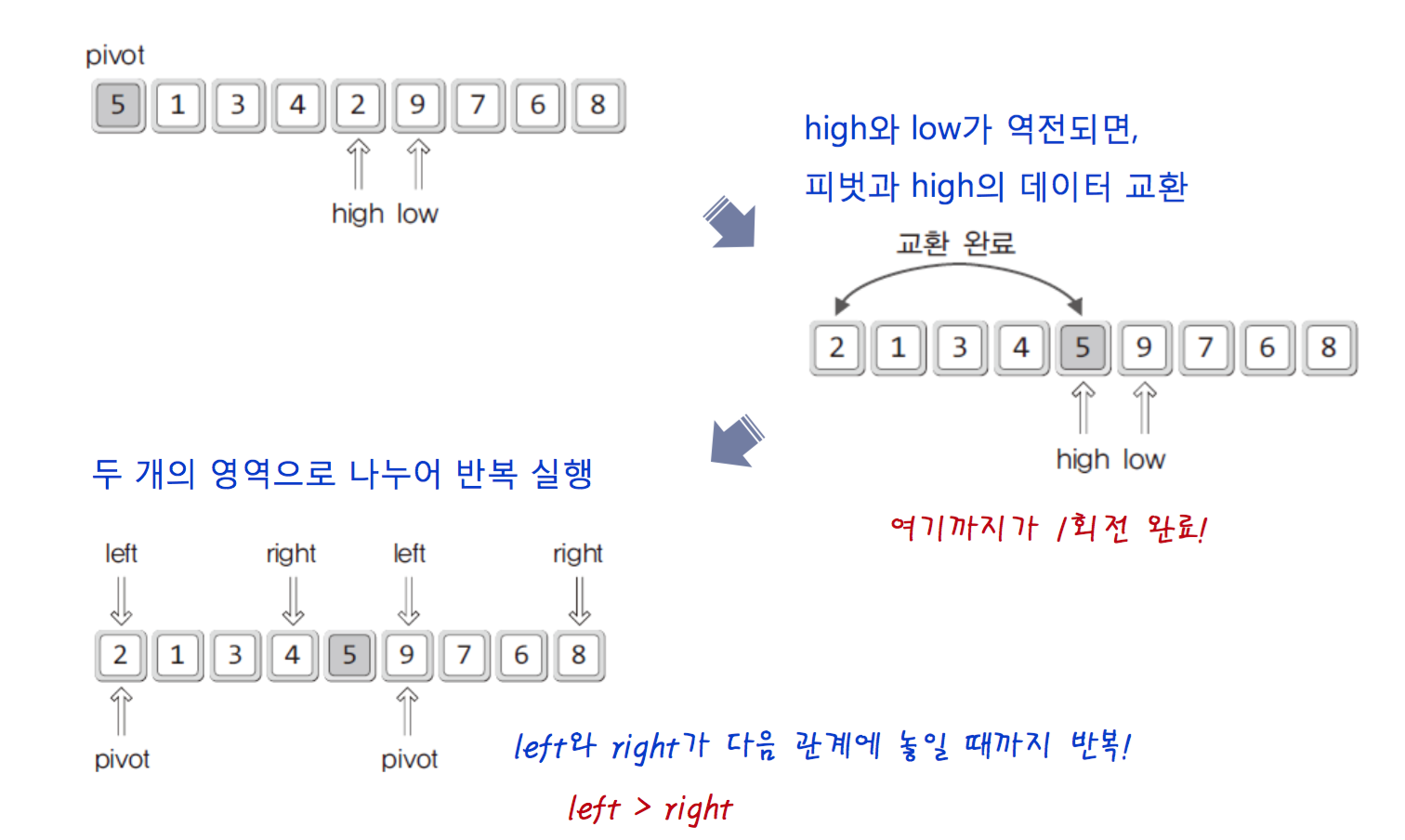
Source code of Quick sorting(increase)
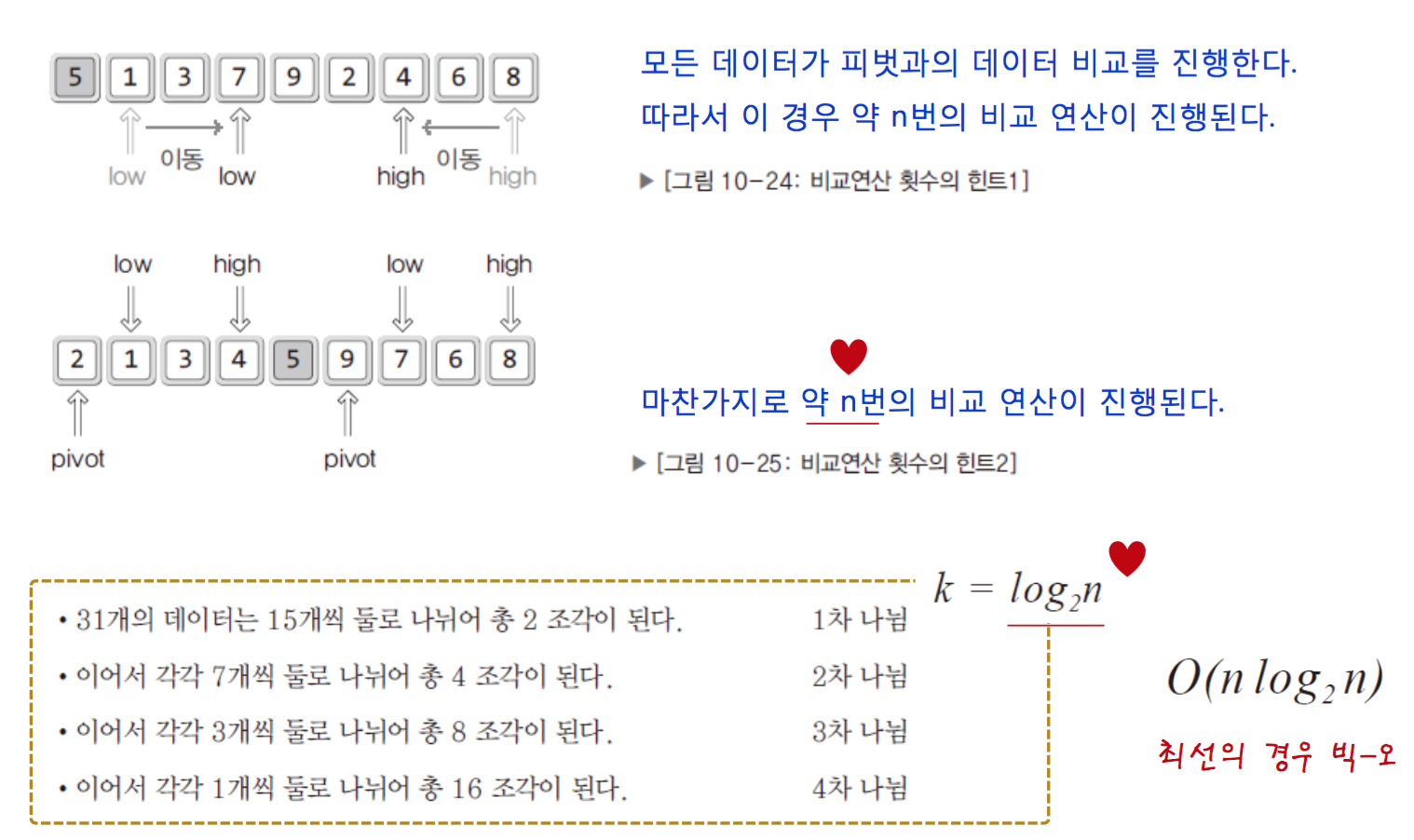
the time complexity is O(nlog N).
This use Divided and Conquer!!!
If array is arranged in order. The time complexity of comparison is O(n^2).

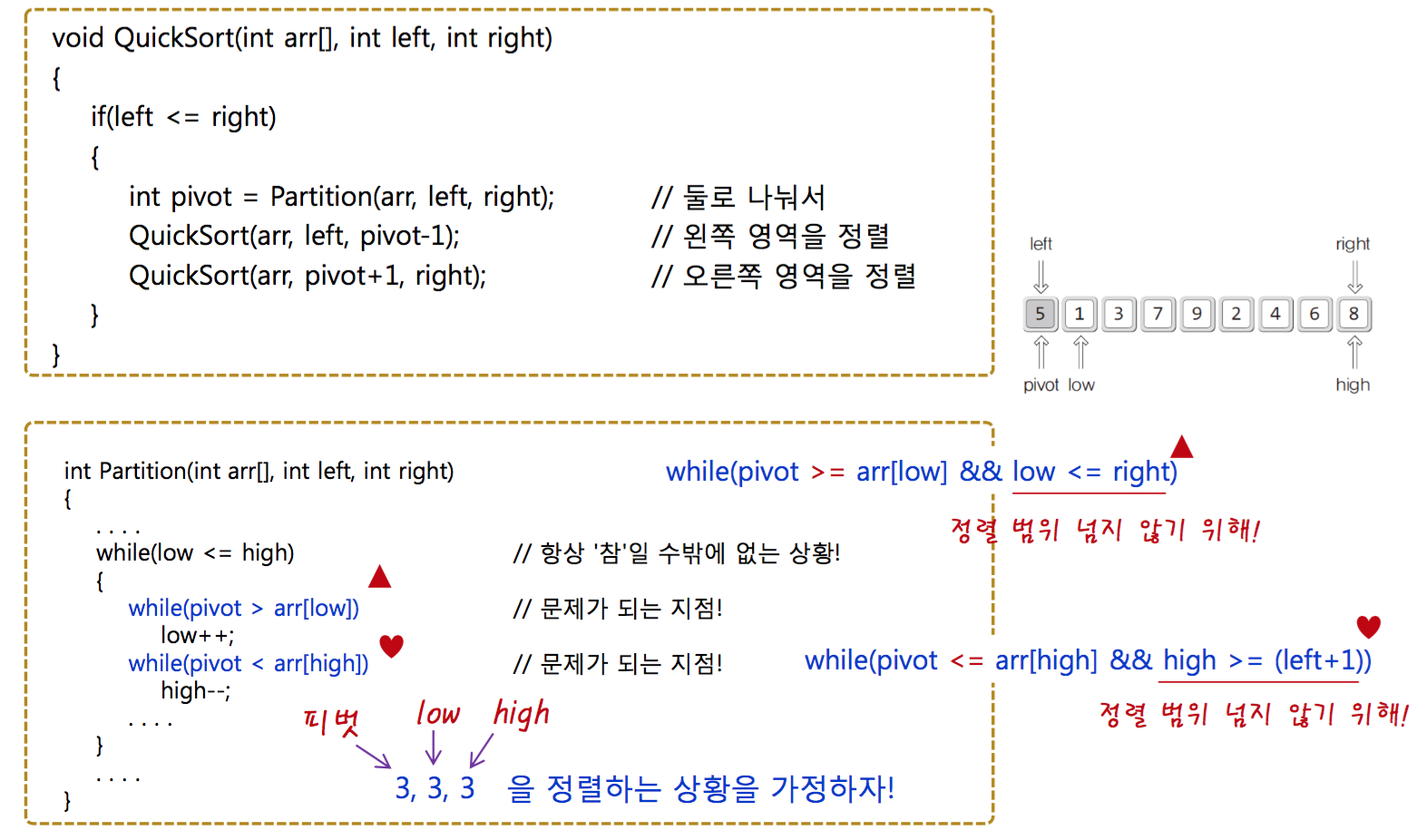
void QuickSorting(int arr[], int left, int right)
{
if(left <= right)
{
int middle = Partition(arr, left, right);
QuickSorting(arr, left, middle-1);
QuickSorting(arr, middle+1, right);
}
}
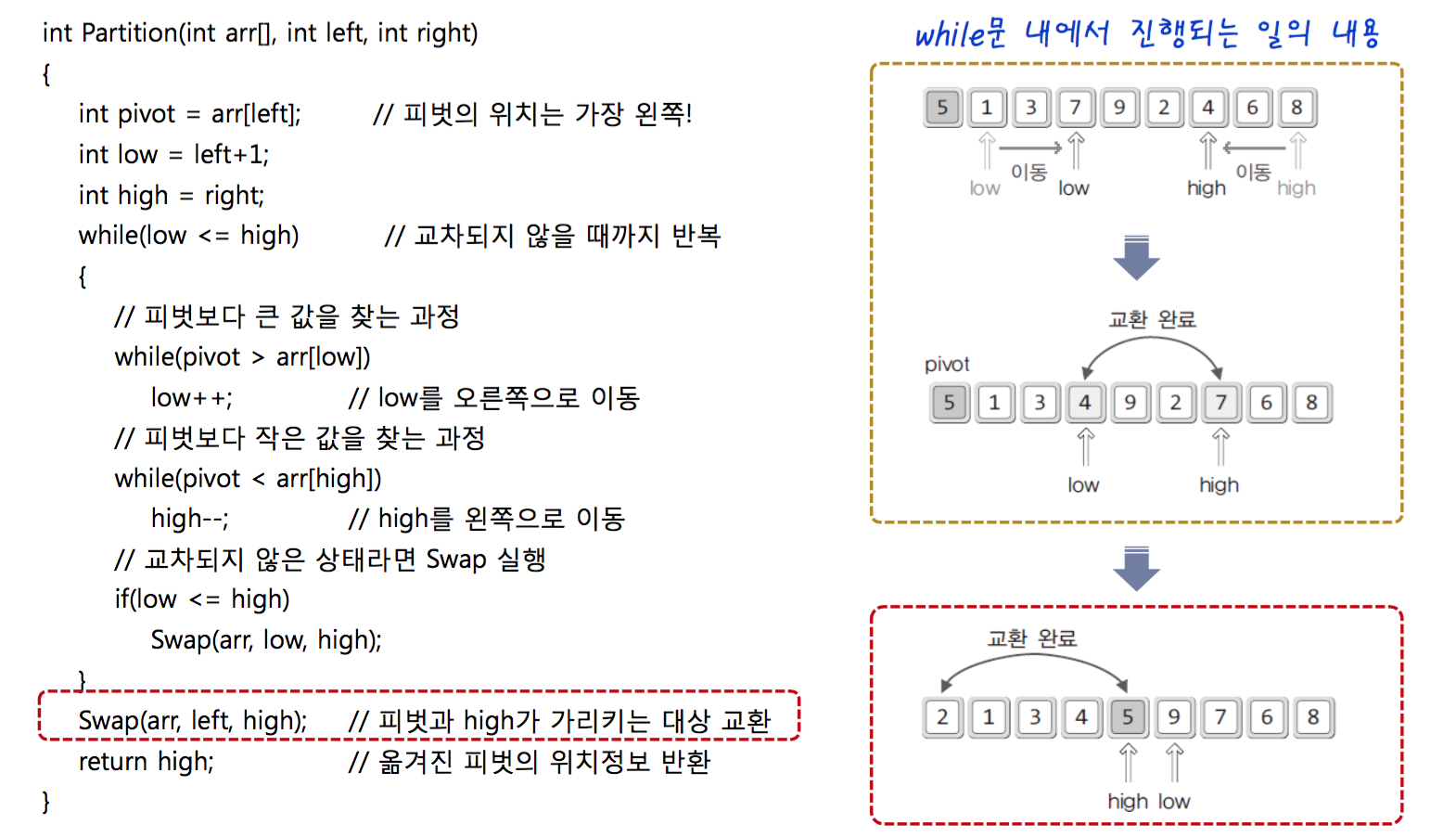
int Partition(arr, left, right)
{
int pivot = left;
int low = left +1;
int high = right;
/// 3 3 3 4 이 경우 생각을 해봐 중복이 허용되는 배열이라면
while(low <= high)
{
if(arr[low] <= arr[pivot] && (low+1) <= right)
low++;
if(arr[high] >= arr[pivot] && (high-1) >= pivot)
high--;
if(low <= high)
swap(arr, low, high);
}
swap(arr, high, pivot);
return high;
}

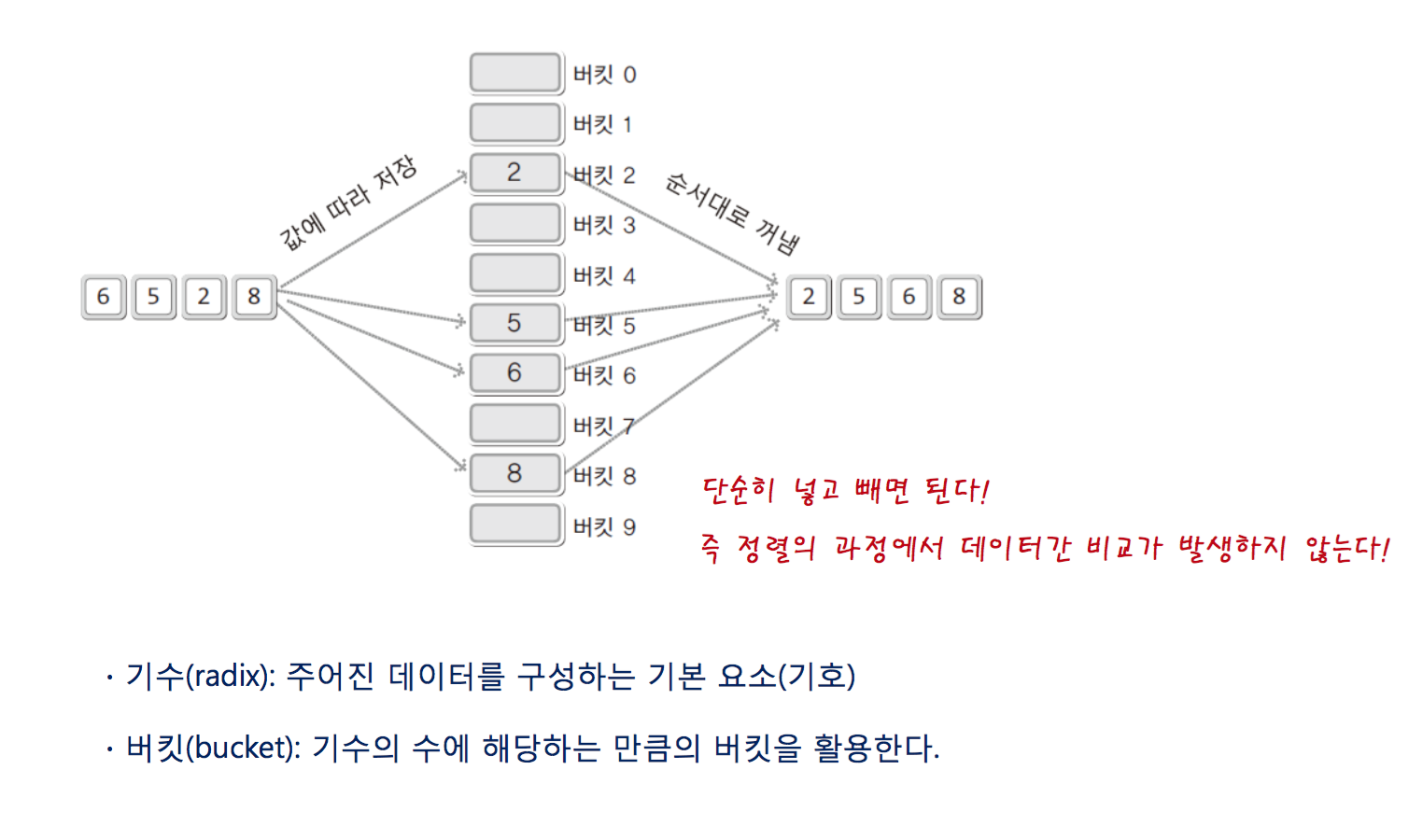
Radix sorting
expression of korean language is 기수정렬이다.
This algorithm uses queue.
This algorithm is much better than sorting algorithm of O(nlogN).
but This algorithm has limitation and it is that length of data is equal.
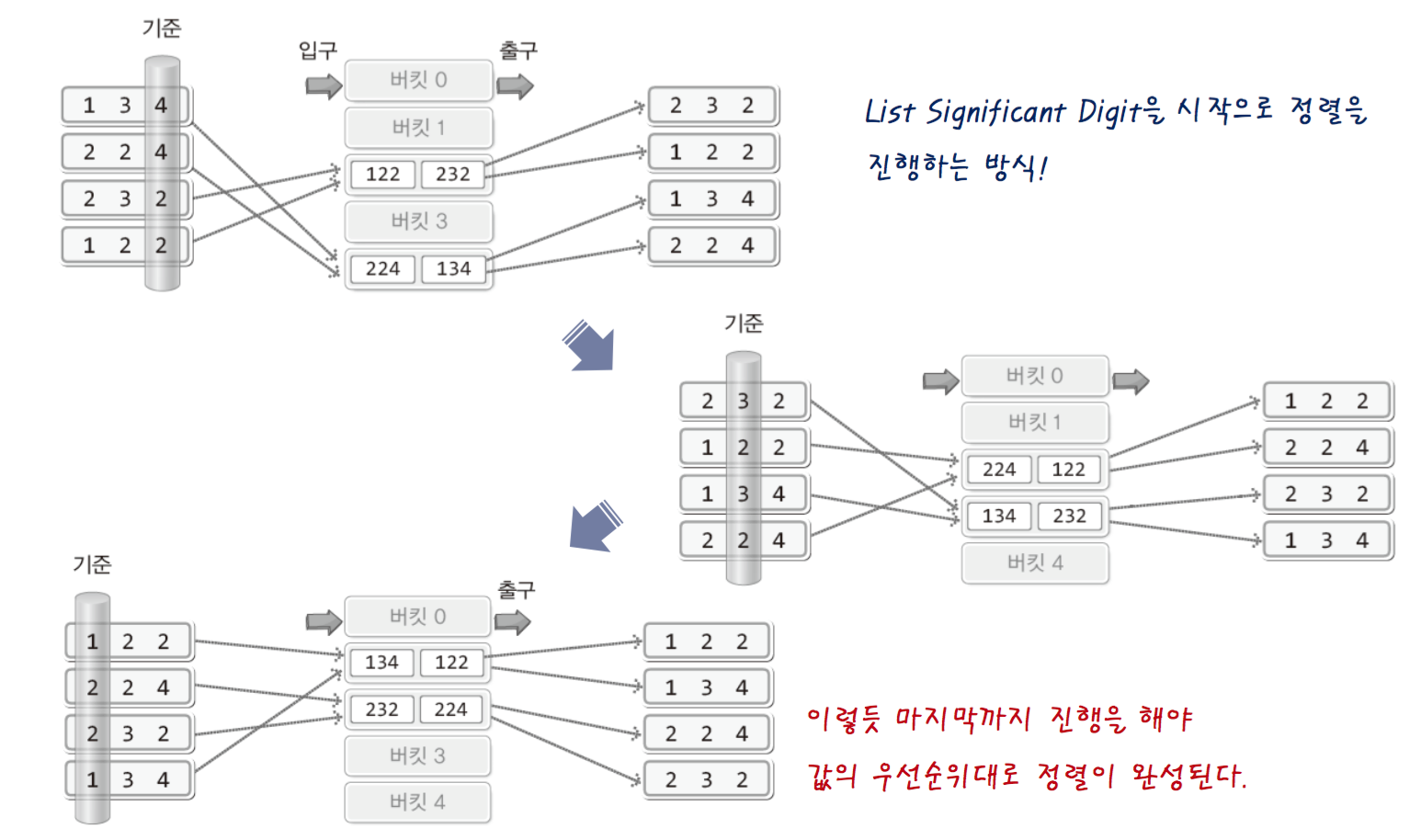
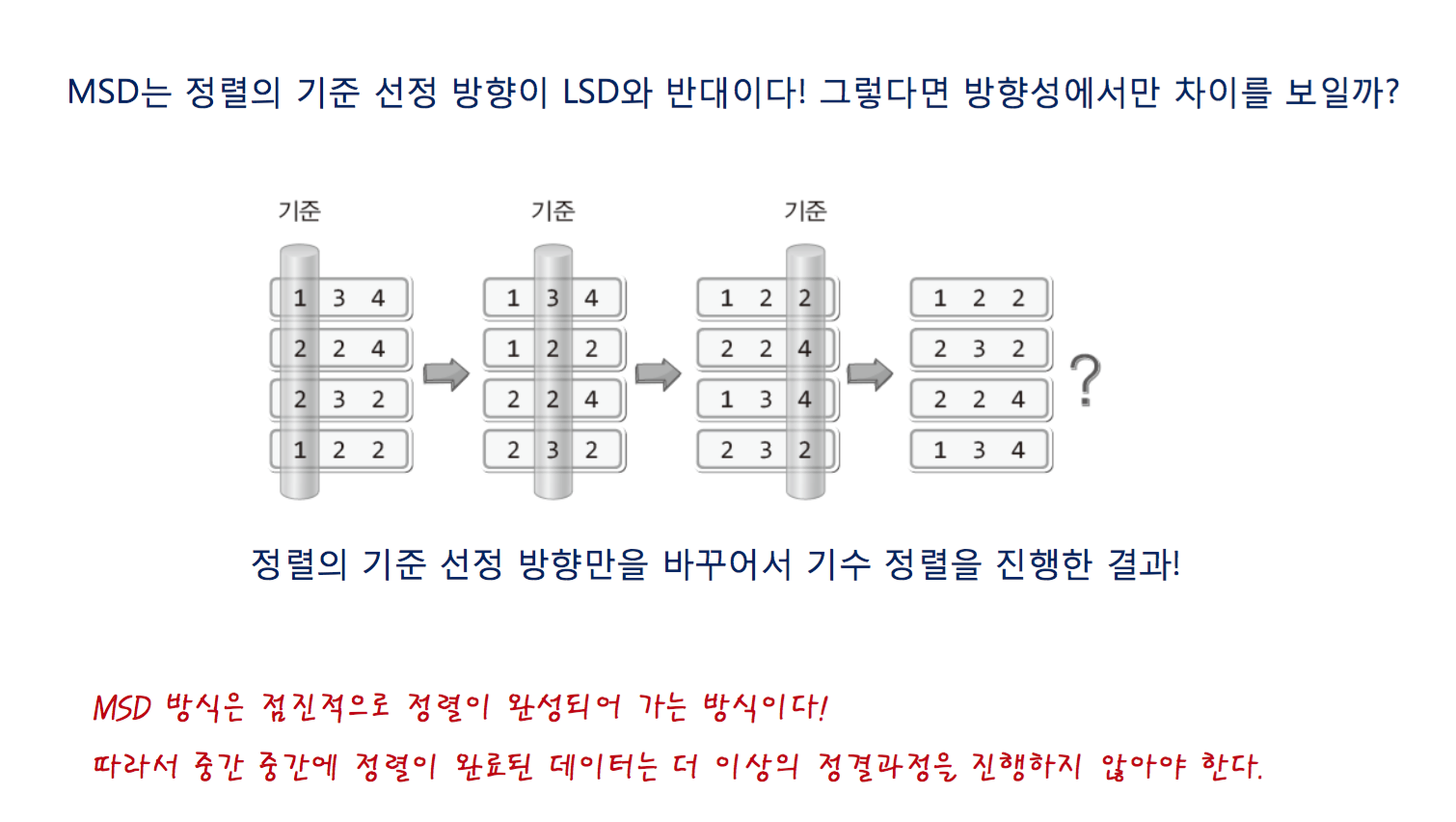
Whether you start the first or the last of digits. big-O is the same.
but starting the first of digits is much easier than the last in making code.

A process of sorting
time complexity is O(ln), if the num of array factor is n and if the length of digit is l.

Source code of Radix sorting(increase - LSD)
this function uses the queue.


#define BUCKET_NUM 10
void RadixSorting(int arr[], int num, int maxLen)
{
Queue buckets[BUCKET_NUM];
int bi;
int pos;
int di;
int divfac =1;
int radix;
for(int bi = 0; bi< BUCKET_NUM ; bi++)
{
QueueInit(&buckets[bi]);
}
// 가장 긴 길이의 데이터 만큼 반복
for(pos = 0 ; pos < maxLen ; pos++)
{
//정렬 대상의 갯수 반큼 반복
for(di = 0 ; di < num ; di++)
{
radix = (arr[di] / divfac) %10
Enqueue(&buckets, arr[di]);
}
for(bi = 0, di = 0; bi < BUCKET_NUM ; bi++)
{
while(!QIsEmpty(&buckets[bi]))
arr[di++] = Dequeue(&buckets[bi]);
}
divfac*=10;
}
}