1-1. What is priority queue
- 이 것을 큐라고 생각을 하면 안된다.
- 그냥 데이터를 우선순위로 순서대로 저장을 하고, 들어간 순서에 상관 없이 우선순의 근거로 데이터를 제거한다.
- 우선순위 큐는 배열, 리스트, 힙을 이용하여 구현을 할 수 있다.
- 이때 우선순위 기준은 이 자료구조를 쓰는 프로그래머가 정하면 된다.


1-2. heap
- 힙은 그냥 완전 이진 트리이다.
- 부모 노드는 자식 노드보다 항상 우선 순쉬가 높아야 한다.
- 근데 형제간의 우선순위는 잘 모른다.
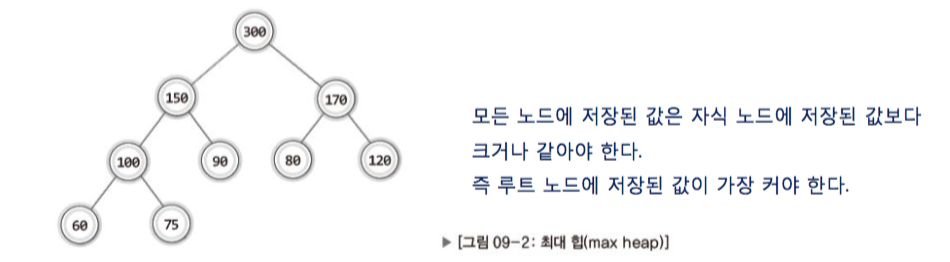
// 최대힙(우선순위가 높다는 것은 노드의 저장 값이 크다는 것이다. - 모든 부모 노드의 저장값이 자식의 노드의 저장값보다 크다. - 즉 루트노드의 값이 가장 크다.
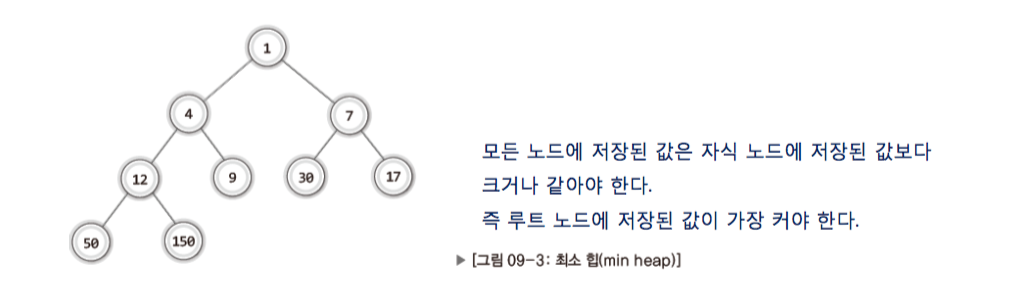
// 최소 힙(우선순위가 높다는 것은 노드의 저장 값이 가장 작다는 것) - 모든 부모 노드의 저장 값이 자식의 노드의 저장값보다 작다. - 즉, 루트 노드의 저장 값이 가장 작다.
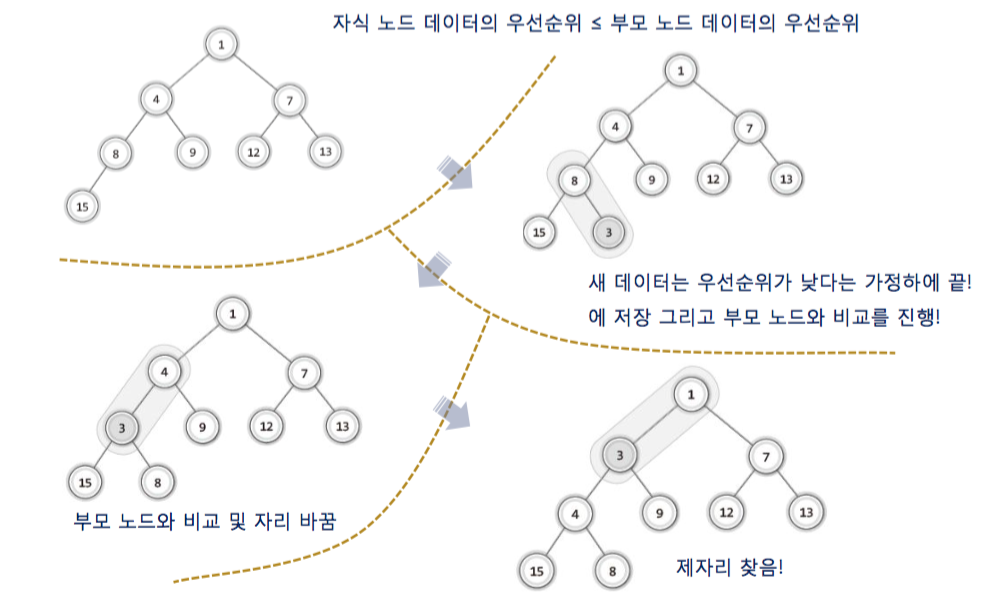
1-3. 힙의 저장과정
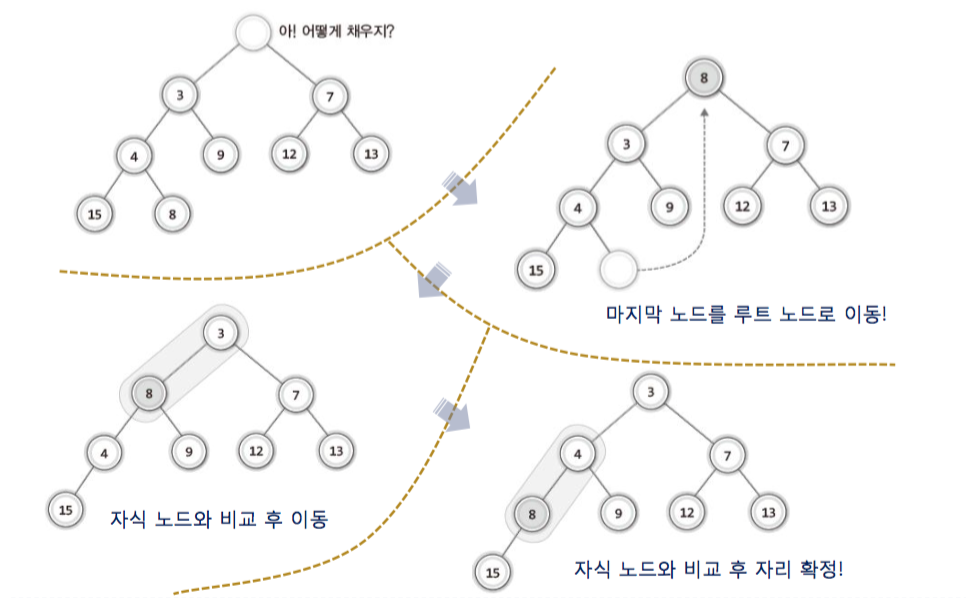
1-4. 힙의 삭제과정
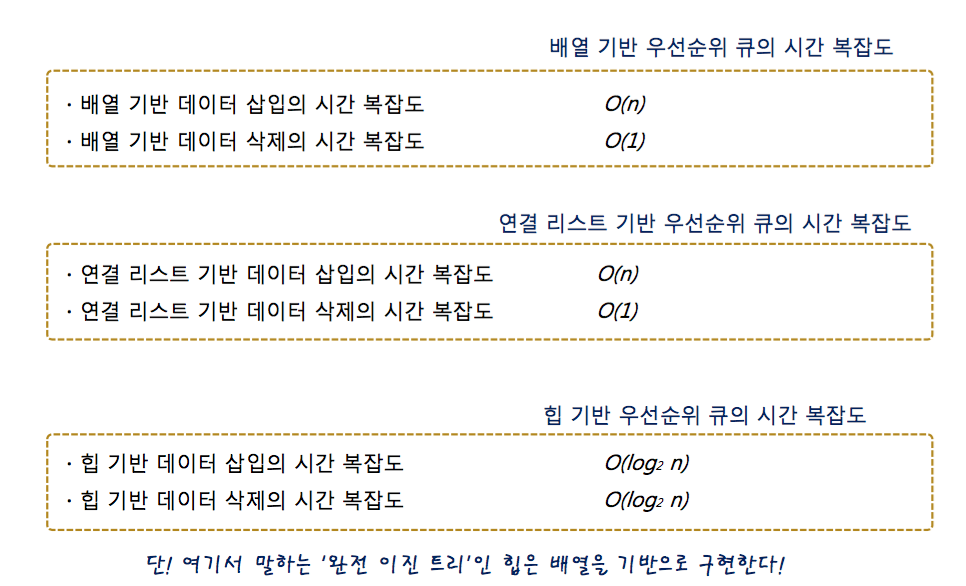
1-5. 삽입과 삭제 과정의 우선수위 큐의 빅오
1-6. Create heap with array

1-7. simply heap source
typedef char HData;
typedef int Priority
typedef struct _heapElem
{
Priority pr; // 값이 적을수록 높은 우선순위
HData data;
}HeapElem;
typedef struct _heap
{
int numOfData;
HeapElem heapArr[HEAP_LEN];
}Heap;
void HeapInit(Heap *ph)
{
ph -> numOfData = 0;
}
int HIsEmpty(Heap *ph)
{
if(ph -> numOfData == 0)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
int GetParentIDX(int idx)
{
return idx/2;
}
int GetLChildIDX(int idx)
{
return 2*idx;
}
int GetRChildIDX(int idx)
{
//return idx*2 + 1;
return GetLChildIDX(idx)+1;
}
// 가장 높은 우선 순위의 자식의 인덱스를 반환 근데
// 배열기반 힙은 0인덱스를 비우고 시작하니
// 노드의 자기 번호가 고유이자 배열의 인덱스
// 힙은 완전이진트리이다. 꼭기억
int GetHiPriChildIDX(Heap * ph, int idx)
{
// 자식이 없으면 0 반환
if (ph -> numOfData < GetLChildIDX(idx))
return 0;
else if(ph -> numOfData == GetLChildIDX(idx))
return GetLChildIDX(idx);
else
{
/// comp 함수는 우선순위를 비교를 위한 함수
if(ph -> comp(ph->heapArr[GetLChildIDX(idx)], ph->heapArr[GetRChildIDX(idx)] < 0)
return GetRChildIDX(idx);
else
return GetLChildIDX(idx);
}
}
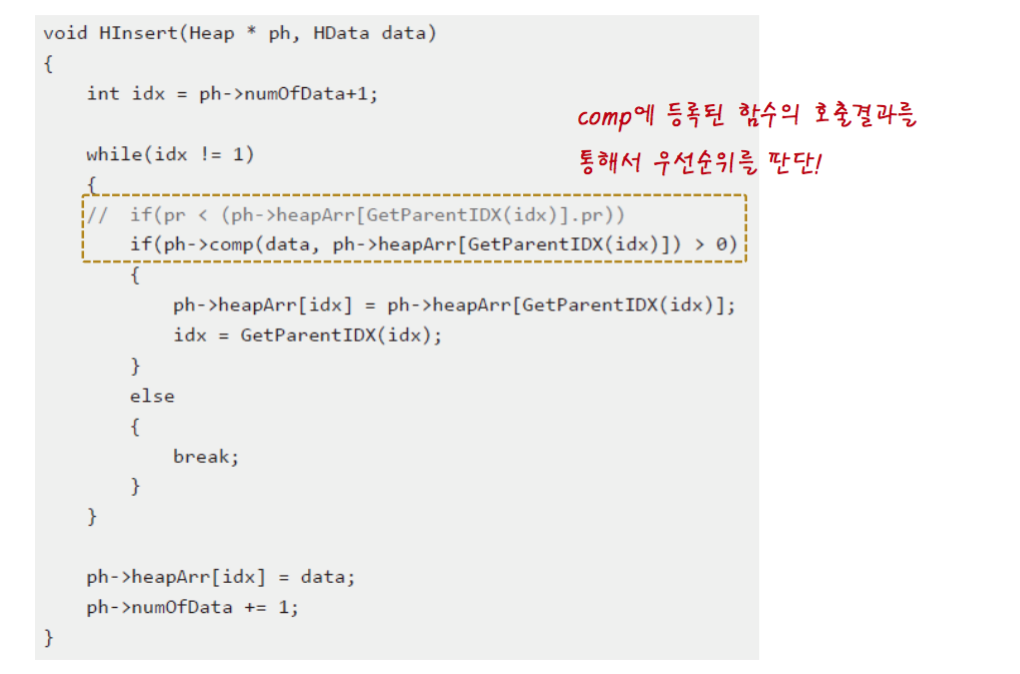
void HInsert(Heap * ph, HData data, Priority pr)
{
int idx = ph -> numOfData +1;
HeapElem nelem = {pr, data};
// new node locates the new while comparing with parent node
while(idx != 1)
{
if(pr < (ph->heapArr[GetParentIDX(idx)].pr)) // if new node is up
{
ph -> heapArr[idx] = ph->heapArr[GetParentIDX(idx)];
idx = GetParentIDX(idx);
}
else
break;
}
ph->heapArr[idx] = nelem;
ph -> numOfData += 1;
}
HData HDelete(Heap *ph)
{
HData retData = (ph -> heapArr[1]).data;
HeapElem lastElem = ph -> heapArr[ph -> numOfData];
int parentIdx = 1;
int chilIdx;
while(childIdx = GetHiPriChildIDX(ph, parentIdx))
{
if (lastElem.pr <= ph->heapArr[childIdx].pr)
break;
ph->heapArr[parentIdx] = ph -> heapArr[childIdx];
parentIdx = childIdx;
}
ph -> heapArr[parentIdx] = lastElem;
ph -> numOfData -= 1;
return retData;
}
/// main function part
int main ()
{
Heap heap;
HeapInit(&heap);
HInsert(&heap, 'A', 1);
HInsert(&heap, 'B', 2);
HInsert(&heap, 'C', 3);
printf("%c \n", HDelete(&heap));
HInsert(&heap, 'A', 1);
HInsert(&heap, 'B', 2);
HInsert(&heap, 'C', 3);
printf("%c \n", HDelete(&heap));
while (!HIsEmpty(&heap))
printf("%c \n", HDelete(&heap));
return 0;
}
// result of main function
A A B B C C
// 데이터 우선순위를 함께 전달하기 보다는 데이터를 근거로 하여 데이터의 우선 순위를 정하는 방식이 더욱 좋을 수도 있다.