this refers to 윤성우의 열혈자료구조.
now I introduce data structure queue.
you make the queue based on array and linkedList.
functionality of queue consists of enqueue and dequeue.
the enqueue puts a data in queue.
the dequeue remove a data from queue
1-1 ADT of queue
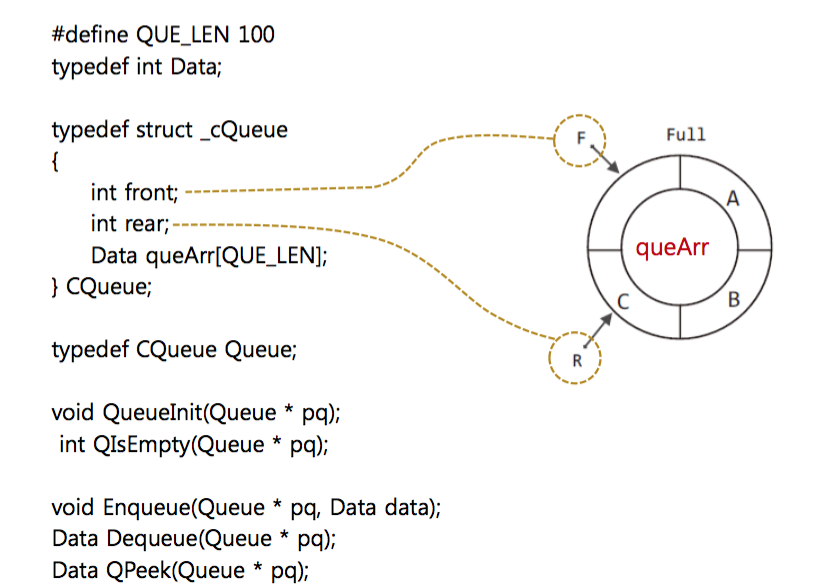
1-1-1. void QueueInit(Queue * pq)
- intialized the queue.(큐를 초기화 한다.)
- you call this function after creating new queue right. (큐 생성후 바로 호출되어야 한다. )
1-1-2. int QIsEmpty(Queue * pq)
- if the queue is empty, this function returns TRUE(1).
- if not, this function returns FALSE(0).
- (큐가 비어 있으면 TRUE(1), 아니면 FALSE(0)을 반환한다.)
1-1-3. void Enqueue (Queue * pq, Data data)
- this stores data int queue.
- 큐에 데이터를 저장한다. 매개변수 data로 전달된 값을 저장한다.
1-1-4. Data Dequeue(Queue * pq)
- this removes the data which is stored the most early.
- this returns data that is removed.
- it guarantees that the queue have one data. when this function is called.
- 저장 순서가 앞선 데이터 삭제, 삭제된 데이터 반환, 이함수 호출시 반드시 하나의 데이터가 저장되어 있어야 한다.
1-1-5. Data QPeek(Queue * pq)
- this just identifies the most early data and don't remove the data.
- it guarantees that the queue have one data. when this function is called.
- 저장 순서가 가장 빠른 데이터 참조만 하고, 삭제는 하지 않는다.
- 이 함수 호출시 데이터가 최소한 하나이상은 존재해야한다.
1-2. implement of queue
1-2-1. concept of queue
- the following picture show you enqueue & dequeue method.
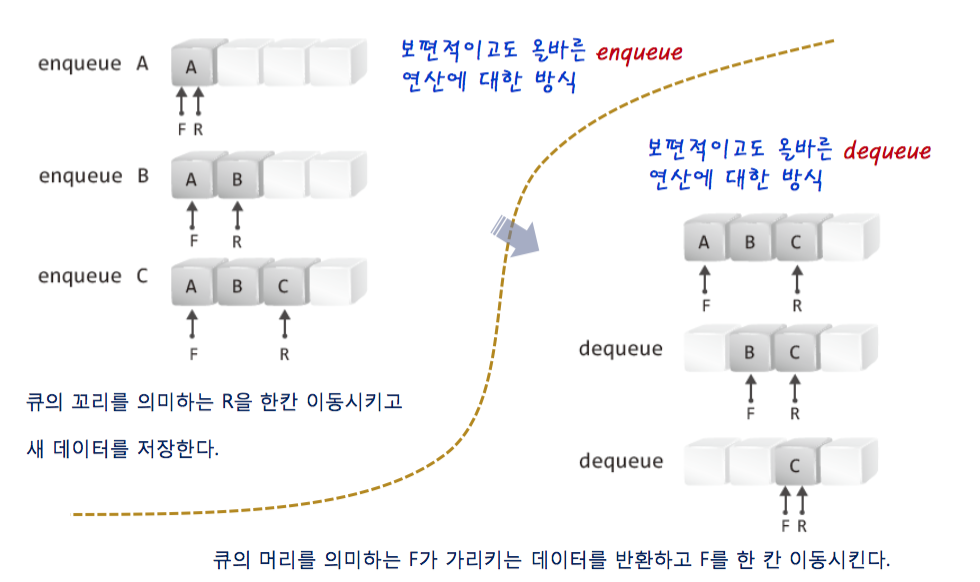
1-2-2. problem of queue based on array.
- after moving R to the right. queue stores a data. but when queue stores D,
- the queue don't go to right, so R moves to the first position(index 0).
- however, as you utilize the circular queue, the problem is easy.
- 배열이다 보니 배열을 크기가 한정되어 있다.
- 그래서 배열 끝가지 데이터를 저장하면 인덱스 0부터 저장을 하던지 배열의 크기를 늘려야 한다.
- 만약 인덱스 0에서 다시 시작을 한다면 이것을 원형 큐라고 한다.

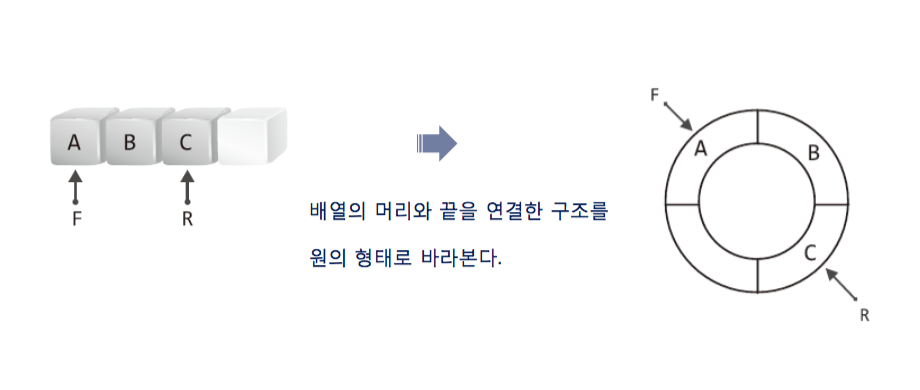
1-2-3. introduction of circular queue
- you think of linear Array as circle.
- 선형 구조인 배열을 원으로 생각을 해라. 그것이 원형 큐의 시작이다.
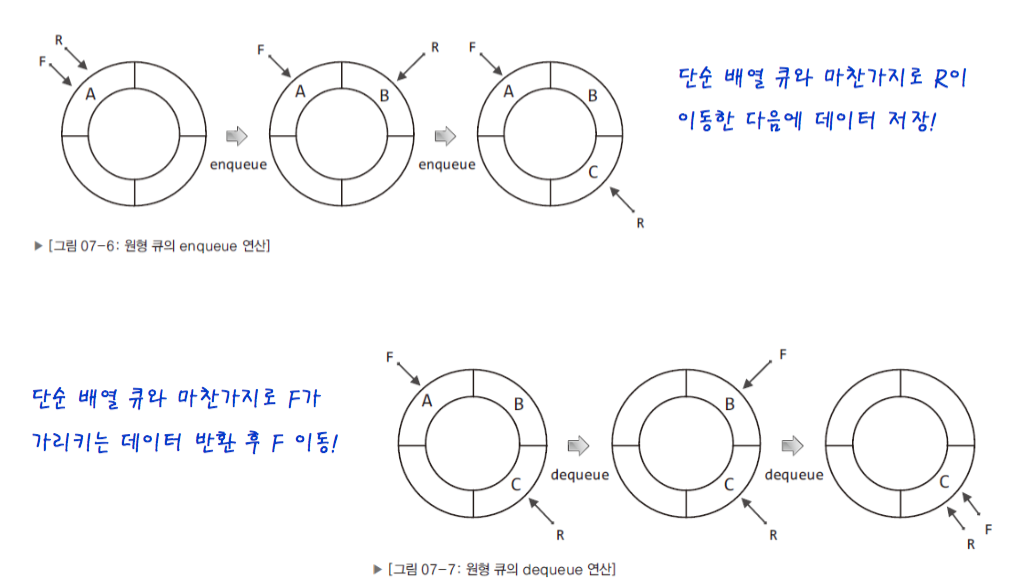
1-2-4. circular queue has a problem
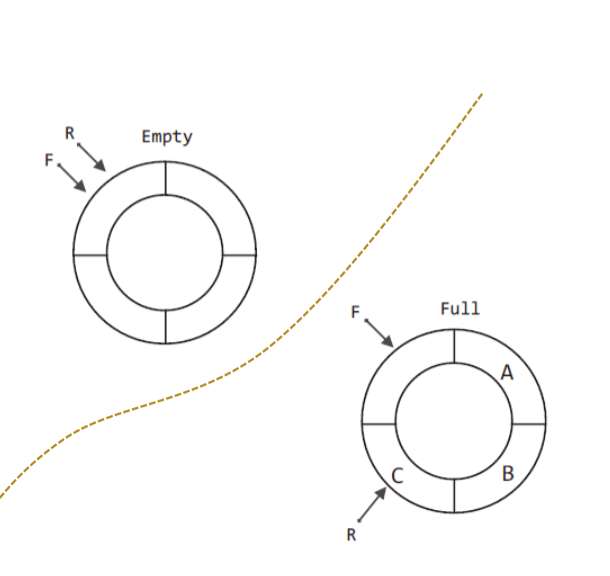
- you make a distinction between the empty queue and the pull queue with R & F.
- but circular queue don't make distinction the both, as follows
- front & rear을 가지고 큐가 비어있는지 아닌지 구분하기 힘들다.
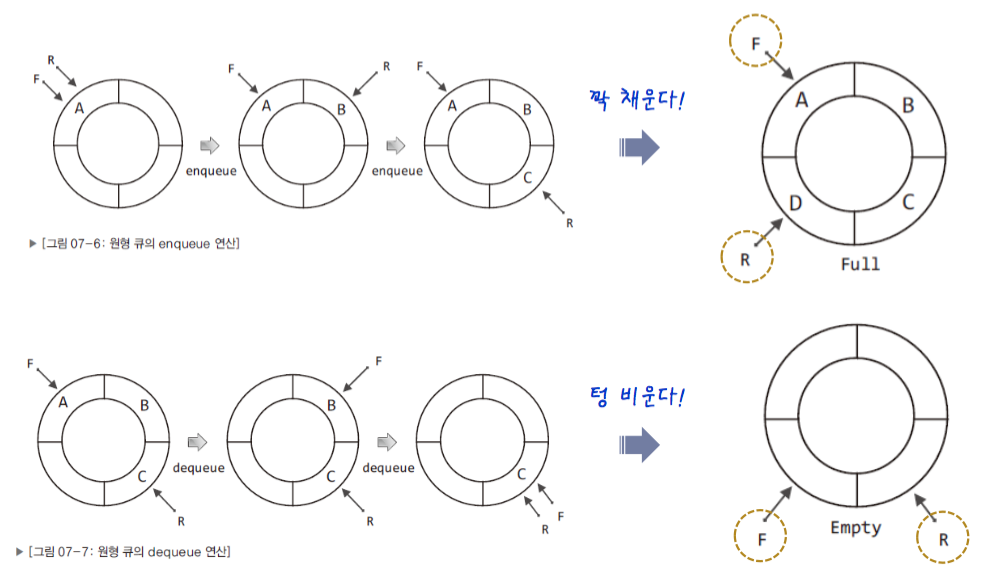
- but we have a solution, as follows.
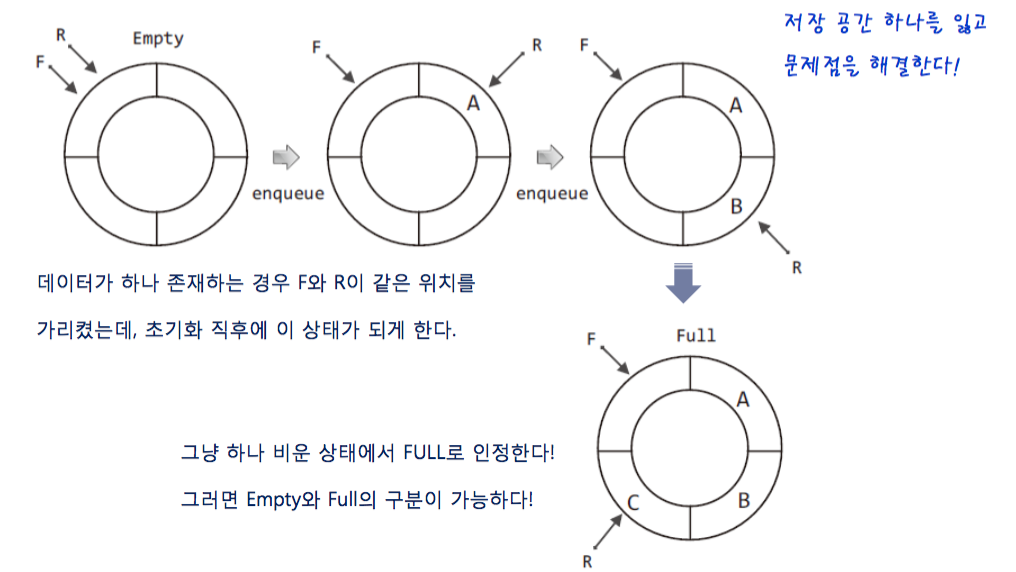
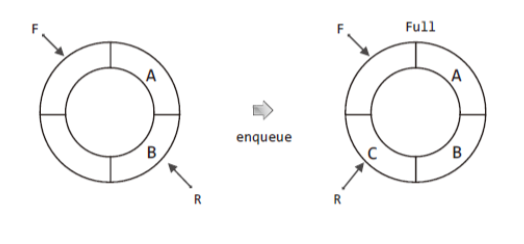
- after the first storage is empty, and you put data in the circular queue.
- So we can make a distinction between the empty queue and the pull queue with R & F.
- if the queue is empty, F & R is located in the same position.
- if the queue is full, F & R is located in the different position.
- 큐의 꽉찬 상태와 아닌 상태를 구분을 위해서 배열의 한칸을 비우고 데이터를 저장한다.
- 이로써 Rear & front가 같다면 큐는 비어있는 상태, 같지 않으면 데이터가 안에 있다는 상태를 나타낸다.
1-2-5. headfile of Source code
1-2-6. Function helping the circular queue
- this function helps the circular queue to decide next index to store a data.
- 아래의 함수가 배열을 원형으로 인식할 수 있게 도와 준다.
// the following is good method. so you apply to other.
// you need to this function to make the circular queue
int NextPosIdx(int pos)
{
if (pos == QUE_LEN -1)
return 0;
else
return pos +1;
}
void QueueInit(Queue * pq)
{
pq -> front =0;
pq -> rear = 0;
}
int QIsempty(Queue * pq)
{
if(pq -> front == pq -> rear)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void Enqueue(Queue * pq, Data data)
{
if(NextPosIdx(pd -> rear) == pq -> front)
{
printf("Queue is full\n");
exit (-1);
}
pq -> rear = NextPosIdx(pq -> rear);
pq -> queArr[pq -> rear] = data;
}
// 큐의 첫번째 인덱스는 비어 있다.
// 꼭 기억
Data Dequeue(Queue * pq)
{
if(QIsEmpty(pq))
{
printf("Queue is empty\n");
exit(-1);
}
pq -> front = NextPosIdx(pq -> front);
return pq -> queArr[pq -> front];
}
// example of main function
int main(void)
{
// initialization queue
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
// put data in the queue
Enqueue(&q, 1);
Enqueue(&q, 2);
Enqueue(&q, 3);
Enqueue(&q, 4);
Enqueue(&q, 5);
// remove data from queue
while (!QIsEmpty(&q))
{
printf("%d ", Dequeue(&q));
}
return 0;
}
// the result of main function
-> 1 2 3 4 5