now I will look into kernel’s lightnvm ioctl(Input Output control, in short), so while studying kernel, I make a note that I learn.
Second Lesson
1-1. ls means list directory contents
I typed “ls -l” in linux computer. for example, The following result is
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 4?? 1 19:43 boot
drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 3260 8?? 26 10:24 dev
drwxr-xr-x. 153 root root 12288 8?? 27 11:53 etc
drwxr-xr-x. 6 root root 103 7?? 6 16:09 home
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 4?? 1 16:46 lib -> usr/lib
[출처] [LINUX] ls -l 명령어 사용시 맨 앞에 나오는 파일 타입|작성자 b1ix
first letter of above result is directory’s & file’s type.
by default Unix have Only 3 type of file
they are :
-
regular file (-)
-
directory file (d)
-the following is special file type.
- Block file(b)
- Character device file(c)
- Named pipe file or just a pipe file(p)
- Symbolic link file(l)
- Socket file(s)
you want to know more. please refer to linuxnix
the following refer to csit.parkland
now I am introducing file permission in linux.
so to check up Permissions, you use “ls -l”,above linux command.
the ls -l command displays a lot of information about the files in the directory
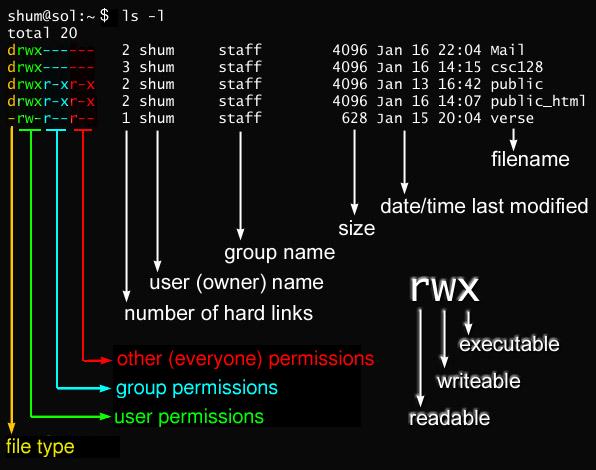
so you need each permision to read, write and excute.
In other words,
To read a file, you need to have read(r) permission for that file.
To write to a file, to modify a file, or to erase a file, yo need to have write(w) for that file.
To run a program or to change to a diretory, you need to have excute(x) permission for that program or directory.
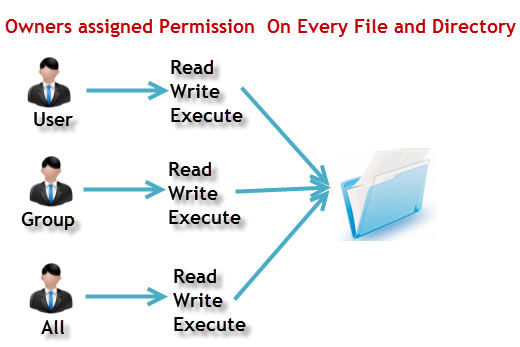
above picture refer to guru99