this refers to 윤성우의 열혈 자료구조.
now I would study Stack.
1-1. Stack’s concept ?
stack is to be Last-in, First-out
basically, the Stack consists of lots of functionality that is push, pop, peek.
the push is to put in the stack.
the pop is to get rid of top from stack.
peek is just to check up top.
1-2. ADT(abstract Data structure, in short) of stack
- based on ADT, you make stack with array, LinkedList.
1-2-1. void StackInit(Stack * pstack)
- initailize the stack.(스택의 초기화를 진행한다.)
- after you make stack, you first have to call this function. (스택을 생성 후, 가장 먼저 호출하는 함수)
1-2-2. int SIsEmpty(Stack * pstack)
- If stack is empty, this function returns TRUE(1).
- If stack is not empty, this function returns FALSE(0).
- 스택이 빈경우 TRUE(1), 아닌 경우는 FASLE(0)을 리턴한다.
1-2-3. Data SPop(Stack * pstack)
- this removes the last item which is stored in stack lately. (마지막 요소를 삭제한다. )
- this function returns a removed item to place to call this function.(삭제된 데이터는 반환한다.)
- to call this function, at least this has one item. (적어도 데이터 하나는 존재해야한 호출시)
1-2-3. Data SPeek(Stack * pstack)
- this just refers to a last item.(그냥 참조만 하는 함수 즉, 마지막에 저장된 요소를 반환만 한다)
- to call this function, at least this has one item.(적어도 데이터 하나는 존재해야 한다 호출시)
1-3. making stack
- first, I design Stack using Array.
1-3-1. the basic structure of Stack
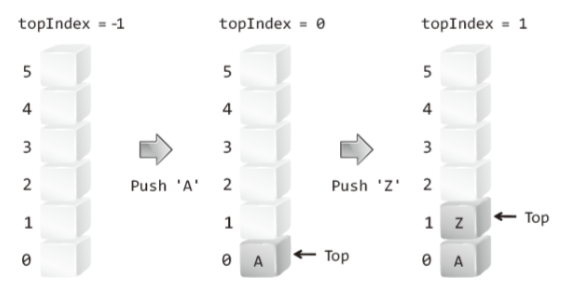
- push : Top up one, then store data in that place.( Top을 위로 하고, 그 위치에 데이터 저장)
- pop : return data of Top, and then Top down one,( Top의 data 반환을 하고, Top을 한칸 내린다.)
1-3-2. the code of Stack
#define TRUE 1
#define FASLE 0
#define STACK_LEN 100
typedef int Data;
// structure of stack based on Array
typedef struct _arrayStack
{
Data stackArr[STACK_LEN];
int topIndex;
} ArrayStack;
typedef ArrayStack Stack;
/// Initailizaiton of Stack
void StackInit(Stack * pstack)
{
pstack -> topIndex = -1;
// just -1 means stack is empty.
// It is enough to move value of topIndex, becaues I overwrite data on before data.
}
/// check up if stack is empty or not
int SIsEmpty(Stack * pstack)
{
// if stack is empty,then this function returns TRUE.
if ( pstack -> topIndex == -1)
return TRUE;
else
return FASLE;
}
// push functionality based on Array
void SPush(Stack * pstack, Data data)
{
pstack -> topIndex += 1;
pstack -> stackArr[pstack -> topIndex] = data;
}
// pop functionality based on Array
Data SPop(Stack * pstack)
{
int rIdx;
if(SIsEmpty(pstack))
{
printf("Stack is empty, so stack error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
rIdx = pstack -> topIndex;
pstack -> topIndex -= 1;
return pstack -> stackArr[rIdx];
}
// Peek functionality based on Array
Data SPeek(Stack * pstack)
{
if(SIsEmpty(pstack))
{
printf("stack Is empty, so Stack error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
return pstack -> stackArr[pstack -> topIndex];
}
//if you use the above function, the following show you example of main function.
int main (void)
{
// initailization of Stack
Stack stack;
StackInit(&stack);
// put data in stack
SPush(&stack, 1);
SPush(&stack, 2);
SPush(&stack, 3);
SPush(&stack, 4);
SPush(&stack, 5);
// extract data from stack
while (!SIsEmpty(&stack))
printf("%d ", SPop(&stack));
return 0;
}
/// result
5 4 3 2 1

-second I design Stack, using LinkedList.
1-3-3. basic concept of stack using LinkedList.
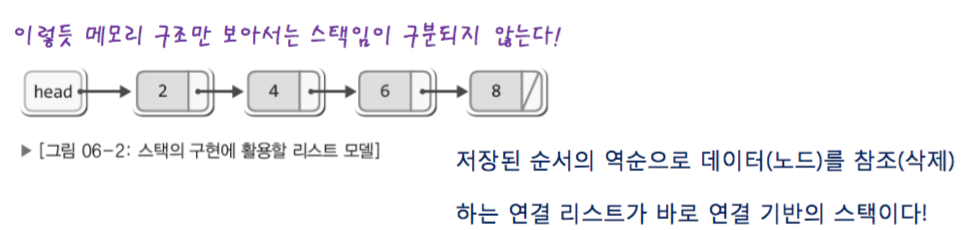
- this stack implements push & pop in LinkedList head.
1-3-4. code of stack using LinkedList.
typedef int Data;
typedef struct _node
{
Data data;
struct _node * next;
} Node;
typedef struct _listStack
{
Node * head;
} ListStack;
typedef ListStack Stack;
void StackInit(Stack * pstack)
{
pstack -> head = NULL;
}
int SIsEmpty(Stack * pstack)
{
if(pstack -> head == NULL)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
Data SPop(Stack * pstack)
{
Node * rnode;
Data rdata;
if(SIsEmpty(pstack))
{
printf("stack is empty so memory error");
exit(-1);
}
rnode = pstack -> head ;
rdata = pstack -> head -> data;
pstack -> head = pstack -> head -> next;
free(rnode);
return rdata;
/// this stack adds new node to head,
// and when deleting node,
// this action happen in linkedList head.
}
// push function
void SPush(Stack * pstack, Data data)
{
Node * newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode -> data = data;
newNode -> next = pstack -> head;
pstack -> head = newNode;
}
//Peek function
Data SPeek(Stack * pstack)
{
if(SIsEmpty(pstack))
{
printf("Stack is empty, soStack Memory Errror!");
exit(-1);
}
return pstack -> head -> data;
}
// utilization of the above stack in main
int main(void)
{
/// stack initialization
Stack stack;
StackInit(&stack);
// insert data into stack
SPush(&stack,1);
SPush(&stack,2);
SPush(&stack,3);
SPush(&stack,4);
SPush(&stack,5);
// extract data from stack
while(!SIsEmpty(&stack))
printf("%d ", SPop(&stack));
return 0;
}
// execute the above main
5 4 3 2 1